Git
Thymeleaf
- java templating engine
- need to add thymeleaf to the pom.xml
- Looping and conditionals
- CSS and js integration
- template layouts and fragments
Project structure
- Thymeleaf template files go in
- src/main/resources/templates
- for web apps, have .html extension
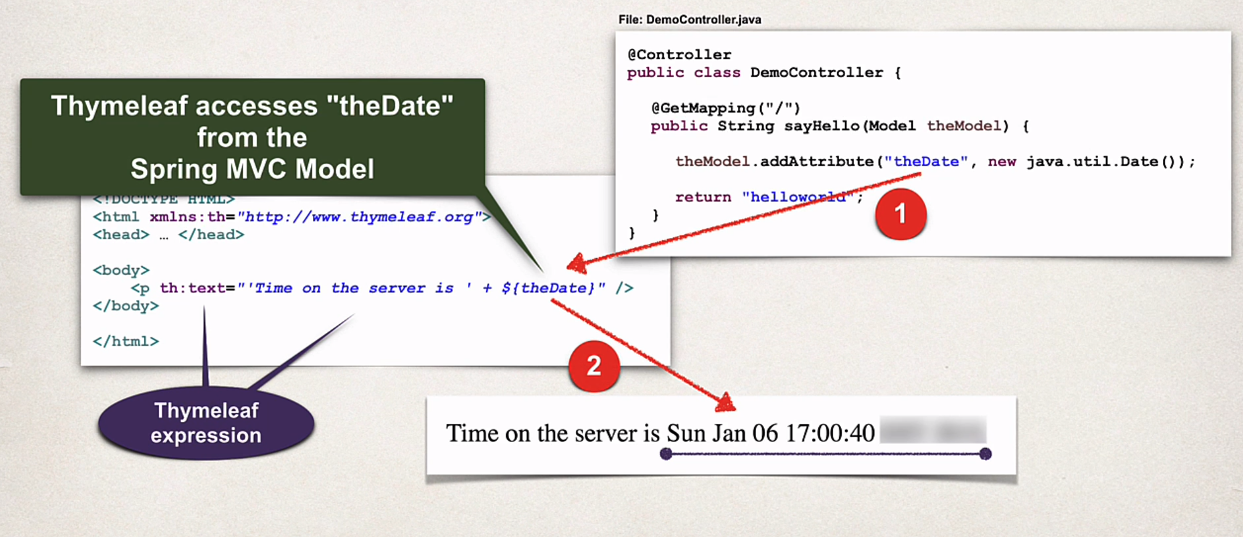
Thymeleaf template (boilerplate)
- thymeleaf expression is between the <p>
- theDate is passed from the controller by the model
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org>
<head> ... </head>
<body>
<p th:text="'Time on the server is ' + ${theDate}" />
</body>
</html>
|
Demo App
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| // has to be @Controller and not @RestController !!!
@Controller
public class DemoController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model){
// add an attribute that can be referenced in the view
model.addAttribute(
"theDate",
new java.util.Date()
);
// looks for src/main/resources/templates/helloworld.html
return "helloworld";
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="'Time on the server is ' + ${theDate}" />
</body>
</html>
|
CSS and Thymeleaf
- spring boot will look for static resources in the directory
- src/main/resources/static
- we can have any folder/file name under static
- CSS is referenced in the html with
1
| <link rel="stylesheet" th:href="@{/css/demo.css}" />
|
- Spring boot will search the following directories for static resources
- /src/main/resources
- /META-INF/resources
- /resources
- /static
- /public
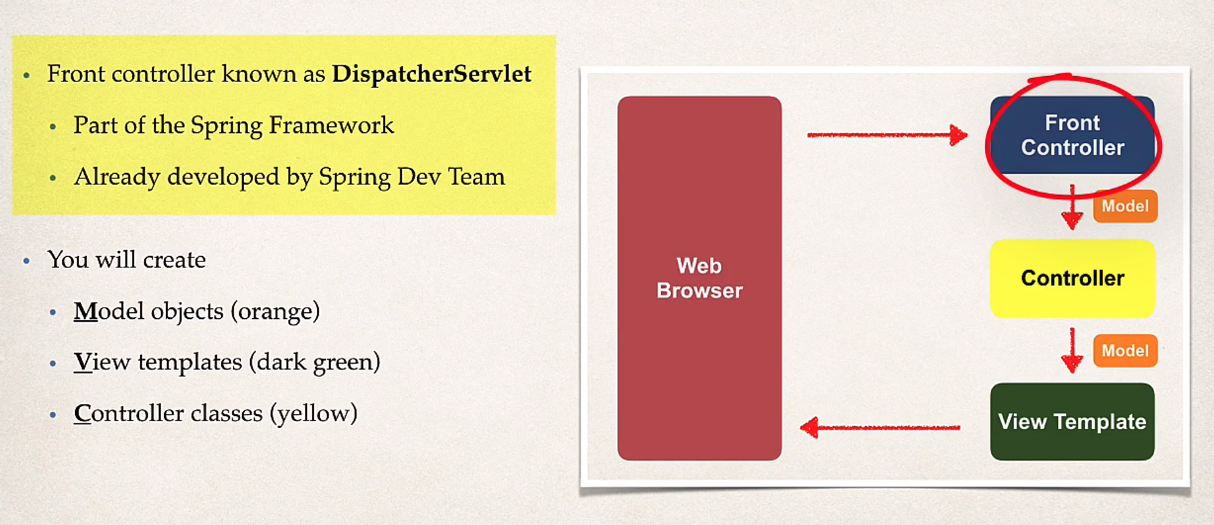
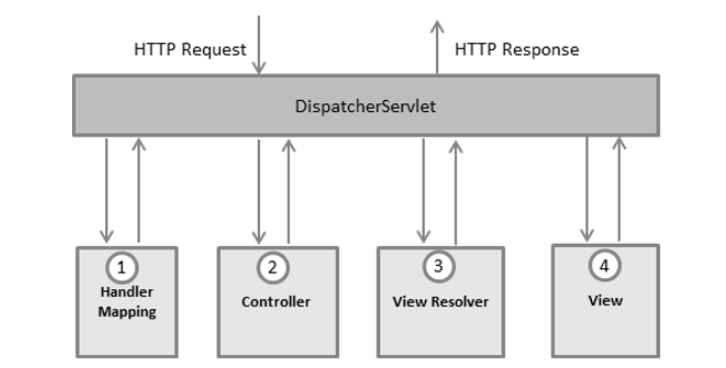
MVC Architecture
Controller class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
// show the form
@RequestMapping(value = "/show", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String showForm(){
return "helloworld-form";
}
// process the form
@RequestMapping("/processForm")
public String processForm(){
return "helloworld";
}
}
|
/show form
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Hello World - Input Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<form th:action="@{/processForm}" method="GET" >
<input type="text" name="studentName"
placeholder="What's your name?" />
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
/processForm
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
Student with name:
<p th:text="${param.studentName}"></p>
</body>
</html>
|
Adding Data to the model
- Simple demo showing controller method taking the query parameter and constructing a message to append to the model before it is passed to the view
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @RequestMapping("/processFormTwo")
public String processFormTwo(HttpServletRequest request, Model model){
// get thename from the query parameters
String name = request.getParameter("studentName");
// convert name to upper case
name = name.toUpperCase();
// construct the message
String message = String.format("HELLO %s, IT IS VERY NICE TO MEET YOU!!!", name);
// add the attribute to the model
model.addAttribute("message", message);
// return the form
return "processForm-2";
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf Demo</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="${message}"></p>
</body>
</html>
|
Binding request parameters with @RequestParam
- We can instead us @RequestParam instead of the above
request.getParameter("param_name") - This will do the exact same as above except it is binded by spring and less effort on our side
public String processFormThree(@RequestParam("studentName"), String name, Model model)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @RequestMapping("/processFormThree")
public String processFormThree(@RequestParam("studentName") String name, Model model){
name = name.toUpperCase();
String message = String.format("HELLO %s, IT IS NICE TO FINALLY MEET YOU", name);
model.addAttribute("message", message);
return "processForm-2";
}
|
A little more about @RequestMapping(), @GetMapping, @PostMapping
- when you use
@RequestMapping("/path") above a method it will accept any http method by default- if you wanted to make it so only Get requests are allowed you could do this
@RequestMapping(value = "/path", method = RequestMethod.GET)
- or you can just use
@GetMapping("/path") instead of having to supply the second parameter - same goest for @PostMapping, @PutMapping etc…
How spring sends data depending on what method is sent
- We have the following code in the form
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <form th:action="@{/processFormThree}" method="GET" >
<input type="text" name="studentName"
placeholder="What's your name?" />
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
|
here is our method signature for the endpoint
1
2
| @GetMapping("/processFormThree")
public String processFormThree(@RequestParam("studentName") String name, Model model){
|
If we hit /show then type in Briana and hit Submit, we will do a GET request to http://localhost:3000/processFormThree?studentName=Briana
- The form data will be sent as Query parameters
however if we change the form to send as POST
1
| <form th:action="@{/processFormThree}" method="POST" >
|
and change @GetMapping to @PostMapping, we will send a POST request to http://localhost:3000/processFormThree with no query parameters and the form data being sent as Request Body
Binding Java object to View
- In the spring controller
- you must add the model attribute before showing the form
- this is a bean that will hold form data for the data binding
- the name must match in the controller and in the view
*{...} is shortcut syntax for ${student.firstName}- when the form is loaded, spring mvc will read student from the model then call the getter methods()
Controller method code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| @GetMapping("/studentForm")
public String studentForm(Model model){
// create student object
Student student = new Student();
// set the properties student ojbect
student.setFirstName("Tresten");
student.setLastName("Pool");
// add the student to the attributes
model.addAttribute("student", student);
// render the form
return "Student/student-form";
}
@PostMapping("/processStudentForm")
public String processStudentForm(@ModelAttribute("student") Student student){
// log the output
System.out.printf("Student\nfirstName: %s\nlastName: %s\n", student.getFirstName(), student.getLastName());
// return the view
return "Student/student-results";
}
|
Field valus are binding with th:field=”*{fieldName}”
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Hello World - Input Form</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Student Registration Form</h3>
<form th:action="@{/processStudentForm}" method="POST" th:object="${student}">
First name: <input type="text" th:field="*{firstName}" />
Last name: <input type="text" th:field="*{lastName}" />
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
just displaying the results
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Student processing page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Student Processing page</h3>
<h4>Student</h4>
First name: <span th:text="${student.firstName}"></span>
<br>
Last name: <span th:text="${student.lastName}"></span>
</body>
|
th:field
- calls the getter methods when displaying the object
- calls the setter methods if used in form to send a post request, it will use the setter methods to change the values of what is in the text field
@ModelAttibute()
- used to get the object from the form
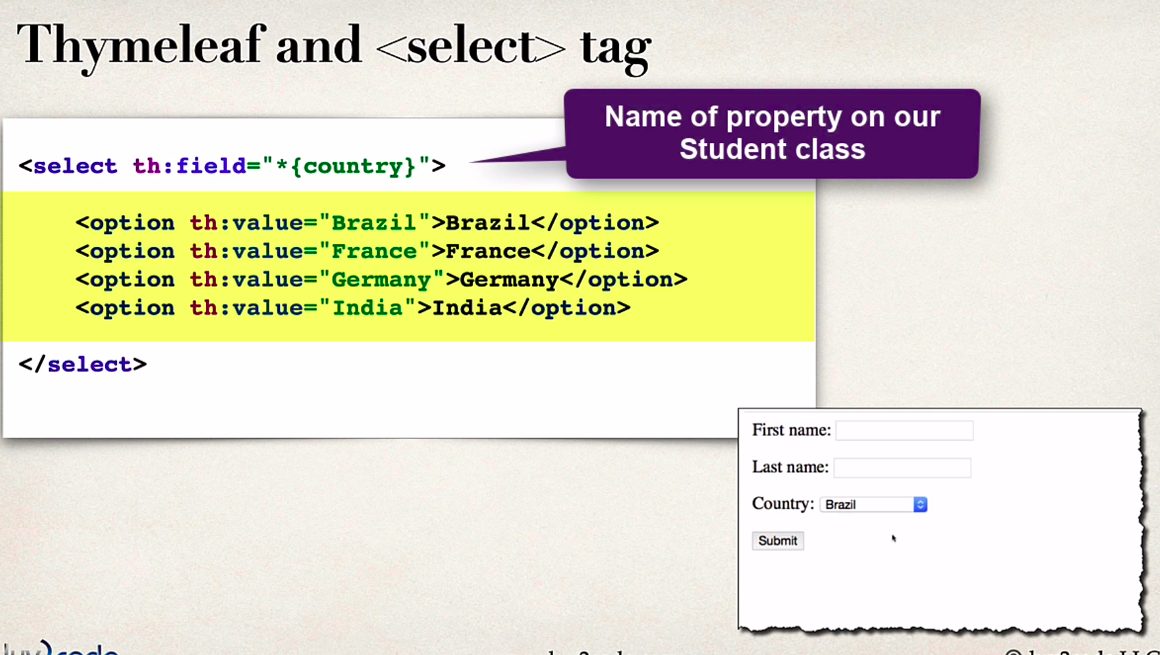
Select with thymeleaf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| <form th:action="@{/processStudentForm}" method="POST" th:object="${student}">
First name: <input type="text" th:field="*{firstName}" />
Last name: <input type="text" th:field="*{lastName}" />
<br>
<select th:field="*{country}">
<option th:value="Brazil">Brazil</option>
<option th:value="France">France</option>
<option th:value="India">India</option>
<option th:value="Germany">Germany</option>
</select>
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
|
- Example below injecting the countries property into the controller then using that in the html file looping over all of the countries
1
| countries=Brazil,France,United States,India,Romania
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| @Controller
public class StudentController {
@Value("${countries}")
private List<String> countries;
@GetMapping("/studentForm")
public String studentForm(Model model){
// create student object
Student student = new Student();
// add the student to the attributes
model.addAttribute("student", student);
// ADD THE COUNTRIES TO THE MODEL
model.addAttribute("countries", countries);
// render the form
return "Student/student-form";
}
|
Loops through all of the country with th:field and th:each
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <body>
<h3>Student Registration Form</h3>
<form th:action="@{/processStudentForm}" method="POST" th:object="${student}">
First name: <input type="text" th:field="*{firstName}" />
Last name: <input type="text" th:field="*{lastName}" />
<br>
<select th:field="*{country}">
<option th:each="tempCountry : ${countries}" th:value="${tempCountry}" th:text="${tempCountry}"></option>
</select>
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <input type="radio"
th:each="language : ${languages}"
th:value="${language}"
th:text="${language}"
th:field="*{favoriteLanguage}"
th:checked="${language} == *{favoriteLanguage}">
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| @Controller
public class StudentController {
@Value("${countries}")
private List<String> countries;
@Value("${languages}")
private List<String> languages;
@GetMapping("/studentForm")
public String studentForm(Model model){
// create student object
Student student = new Student();
// set the properties student ojbect
student.setFirstName("Tresten");
student.setLastName("Pool");
student.setFavoriteLanguage("Zig");
// add the student to the attributes
model.addAttribute("student", student);
// add the countries to the model
model.addAttribute("countries", countries);
// add the languages to the model
model.addAttribute("languages", languages);
// render the form
return "Student/student-form";
}
|
Validation
Valiation Annotations
- below is a table of some of the most common validation annotations
| Annotation | Contact |
|---|
| @NotNull | Value cannot be null |
| @Min | Must be num >= value |
| @Max | Must be num <= value |
| @Size | Size must match given size |
| @Pattern | Must match a regular expression pattern |
| @Future / @Past | Date must be in future or past given date |
Customer class
- here we use some annotations that will be used for validations later
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class Customer {
@NotNull(message = "is required")
@NotBlank(message = "cannot be blank")
private String firstName;
@NotNull(message = "is required")
@NotBlank(message = "cannot be blank")
private String lastName;
// constructors
// getters and setters
}
|
Customer controller methods
Show form
- th:action=”@{/processedForm}”
- where the form will go to
- th:object=”@{customer}”
- the variable of the object that the model passed in
- th:if=”${#fields.hasErrors(‘lastName’)}
- checks if the fields object has an errors for lastname
- fields is an object that is created by the Validator in springboot automatically
- th:error=”*{lastName}”
- prints out the errors that the validator has for lastName
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Customer Form</title>
<style>
.error{
color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<i>Fill out the form. Asterisk (*) means required.</i>
<br><br>
<form th:action="@{/processForm}" th:object="${customer}" method="POST">
First name: <input type="text" th:field="*{firstName}">
<br><br>
Last name (*): <input type="text" th:field="*{lastName}">
<!-- Add Error message if present -->
<span th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('lastName')}"
th:errors="*{lastName}"
class="error">
</span>
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
|
@InitBinder removes whitespace
- works as a pre-processor
- pre-processes each web request to the controller
@InitBinder method in the controller
- WebDataBinder as an argument
- .registerCustomEditor(String.class, stringTrimmerEditor) to maniupulate all Strings coming in from requests
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @InitBinder
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder webDataBinder){
System.out.println("in initbinder");
// creating the string trimmer
StringTrimmerEditor stringTrimmerEditor = new StringTrimmerEditor(true);
// saying that for all Strings that come in, register the stringtrimmereditor to be ran on it
webDataBinder.registerCustomEditor(String.class, stringTrimmerEditor);
}
|
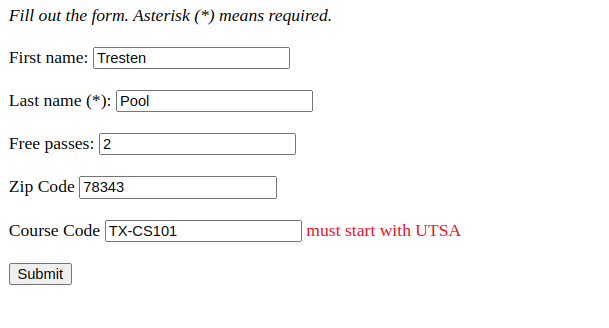
- Trying to make an integer required
- We are getting this because it is trying to convert an int to a string to trim all of the whitespace that we had configured in the @InitBinder
- To fix we can make it an Integer instead of an int and that will be able to be converted to a String with the .toString()
I have the following code in the model where I define an integer with the following annotations
1
2
3
| @Range(min = 0, max = 10, message = "Must be between 0 and 10")
@NotNull(message = "free passes is required")
private int freePasses;
|
- I am getting the following error after trying to submit
- it is trying to convert a String –> int
Fix
- This can be fixxed by using the Integer class instead of primitive int
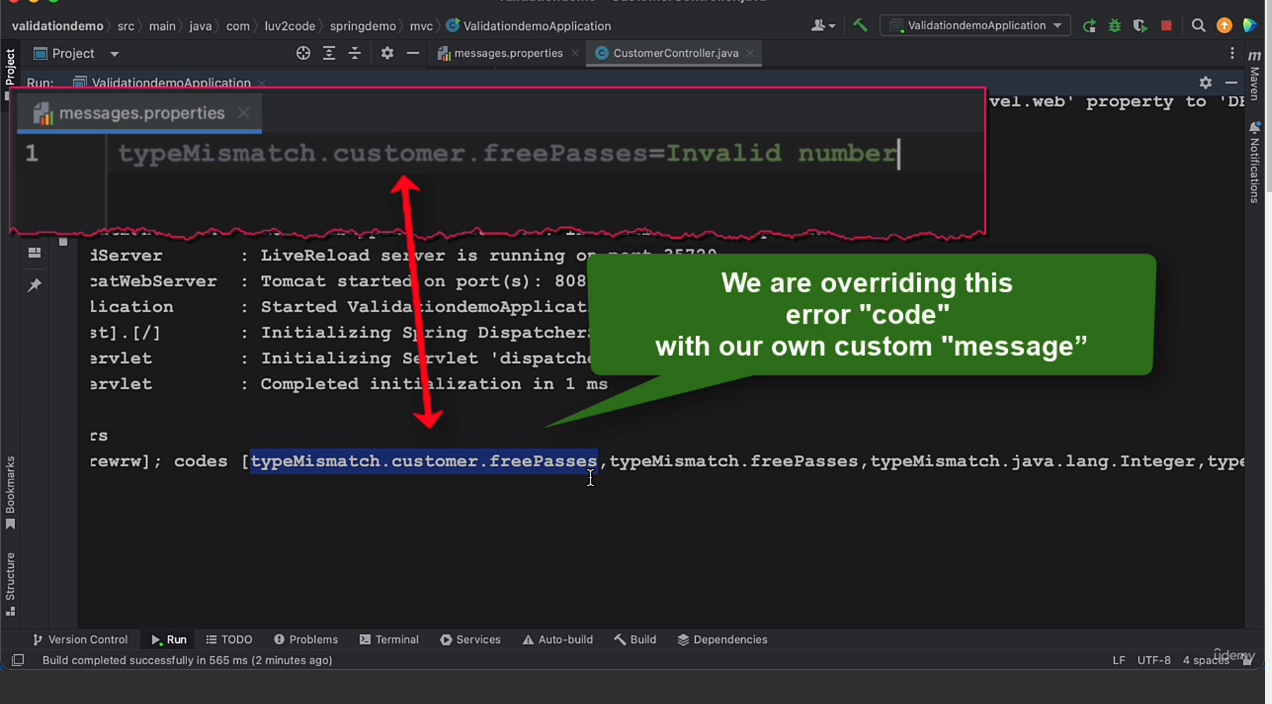
Custom Error messages
- filename and location has to be —> src/main/resources/messages.properties
1
2
3
| # format explained below vvv
# error type . spring model attribute name . field name . our custom error message
typeMismatch.customer.freePasses=Invalid number
|
HTML file
- in the html file you can just reference errors like normal
1
2
3
4
5
| <!-- Free passes errors -->
<span th:if="${#fields.hasErrors('freePasses')}"
th:errors="*{freePasses}"
class="error">
</span>
|
How to get custom error codes
- How do I know what the error code is like in the previous example typeMismatch.customer.freePasses=Invalid number
- We can get it by printing the BindingResult to the console then using that in the messages.properties file
- Once we get the error message we can put it in our messages.properties file for the custom error message
System.out.println("Binding result: " + bindingResult.toString());
Creating Custom validation rule
- we want a custom validation to make sure the course code starts with LUV
Steps 1. Create the custom annotation
- comments in the code below describe what each peice is used for
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| // tells the annotation what class that is going to validate this annotation
@Constraint(validatedBy = CourseCodeConstraintValidator.class)
// tells the jvm what the annotation can be used for
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD})
// The retention policy determines how long the annotated annotation should be retained or available in the compiled class files and at runtime.
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
// it indicates that this annotation should be included in the generated Javadoc and other documentation tools.
@Documented()
public @interface CourseCode {
// default course code
String value() default "LUV";
// default error message
String message() default "must start with LUV";
// define default groups
Class<?>[alt-text] groups() default {} ;
// define default payloads
// payloads provide custom details about the validation failure(security level, error code, etc..)
Class<? extends Payload>[alt-text] payload() default {};
}
|
Step 2: Create the Validator Class
- must implement ConstraintValidator
- <Annotation, Type that we will check against>
- Has 2 methods we need to override
- initialize()
- isValid()
- checks to see if the code passed in is the same as our prefix that was set
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| // <Annotation class, variable that we will use in the isValid method()
public class CourseCodeConstraintValidator implements ConstraintValidator<CourseCode, String> {
// assign this when the annotation is initialized
private String coursePrefix;
@Override
public void initialize(CourseCode courseCode) {
coursePrefix = courseCode.value();
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(String codeToCheck, ConstraintValidatorContext constraintValidatorContext) {
// return true if no value was supplied
if(codeToCheck == null){
return true;
}
// return true if the code supplied starts with the course prefix, false otherwise
return codeToCheck.startsWith(coursePrefix);
}
}
|
Example:
Student class
1
2
| @CourseCode(value = "UTSA", message = "must start with UTSA")
private String courseCode;
|