Udemy Spring boot course: Section 5 REST Api Security
- Github Repo
- Section goals
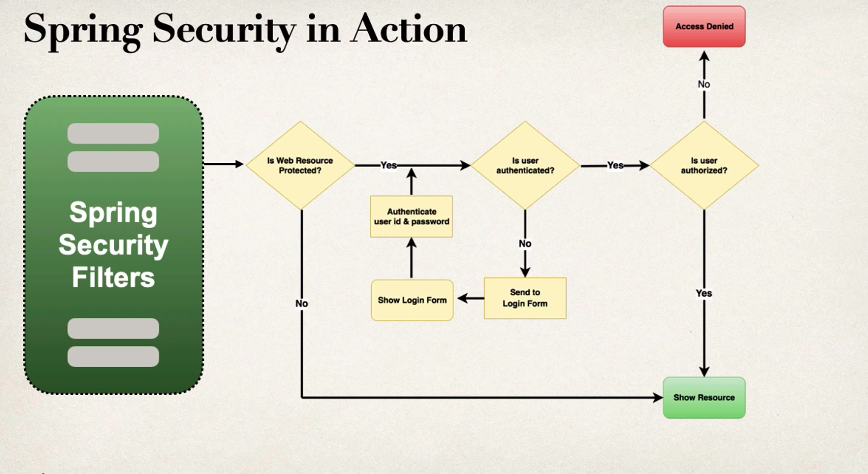
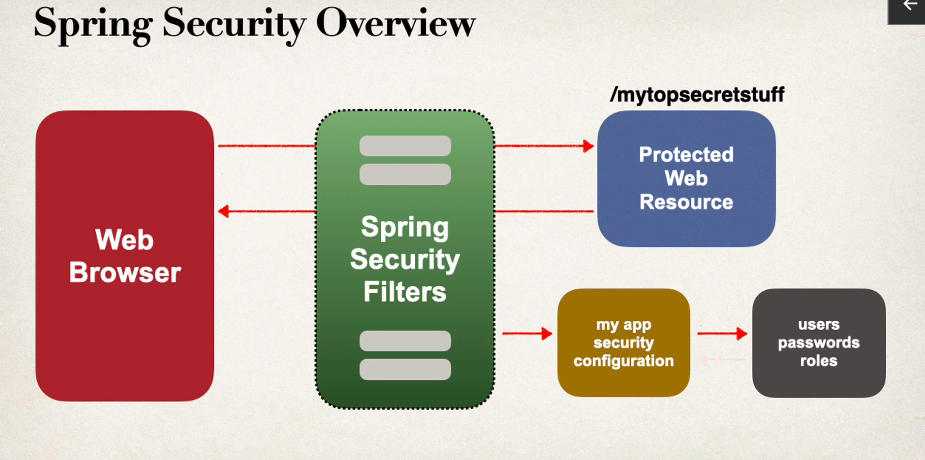
- Spring Security Model
- Enabling Spring Security
- Different types of authentication methods for spring security
- Adding in memory users to Spring Security
- Restrict URLS based on Roles
- Security Filter Chain
- DB authentication
Github Repo
Section goals
- Secure Spring boot REST APIs
- Define users and roles
- protect urls
- protect urls based on roles
- store users, passwords and roles in DB (plain-text -> encrypted)
- Just the basics, not too in depth
Spring Security Model
- Implemented using Servlet filters in the background
- Two methods of securing an app:
- Declarative
- Programmatic
Declarative
- Define security constraints in configuration
- @Configuration
- Provides separation of concerns between application code and security
Programmatic
- spring security provides an API for custom application codding
- more customizable for specific app requirements
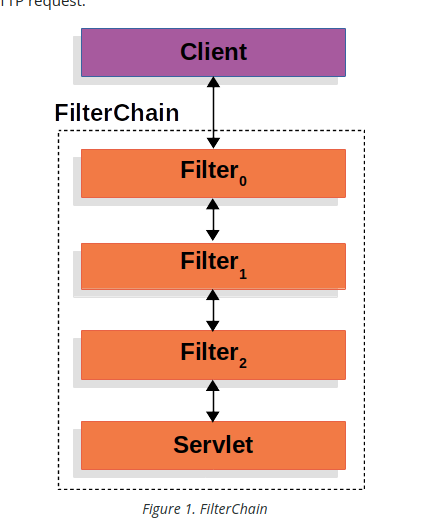
Servlet Filters
- Servlet filters are used to pre-process / post-process web requests
- Servlets route web requests based on security logic
- spring provides a bulk of security functionality with servlet filters
Spring Security Filters Workflow
Enabling Spring Security
- just add the dependency to your pom.xml
- This will automatically secure all endpoints for the application
- this will prompt for a username and password
- default username: user
- default password: generated in the console at startup
- or you can set your own username and password by editting the application.properties file
1
2
spring.security.user.name=username
spring.security.user.password=mypassword123
Different types of authentication methods for spring security
Adding in memory users to Spring Security
- spring security in memory docs
- We can in memory users with the following
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
@Configuration
public class DemoSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public InMemoryUserDetailsManager userDetailsManager(){
// john
UserDetails john = User.builder()
.username("john")
.password("{noop}test123")
.roles("EMPLOYEE")
.build();
// mary
UserDetails mary = User.builder()
.username("mary")
.password("{noop}test123")
.roles("EMPLOYEE", "MANAGER")
.build();
// susan
UserDetails susan = User.builder()
.username("susan")
.password("{noop}test123")
.roles("EMPLOYEE", "MANAGER", "ADMIN")
.build();
return new InMemoryUserDetailsManager(john, mary, susan);
}
}
Authorize with the VSCode Rest Client
- in order to authenticate with the api you can add the following to the endpoints.rest file in vscode
Authorization: Basic john:test123
@host=localhost
@port=3000
###
# Get all employees
GET http://:/api/employees?sort=email,asc
Authorization: Basic john:test123
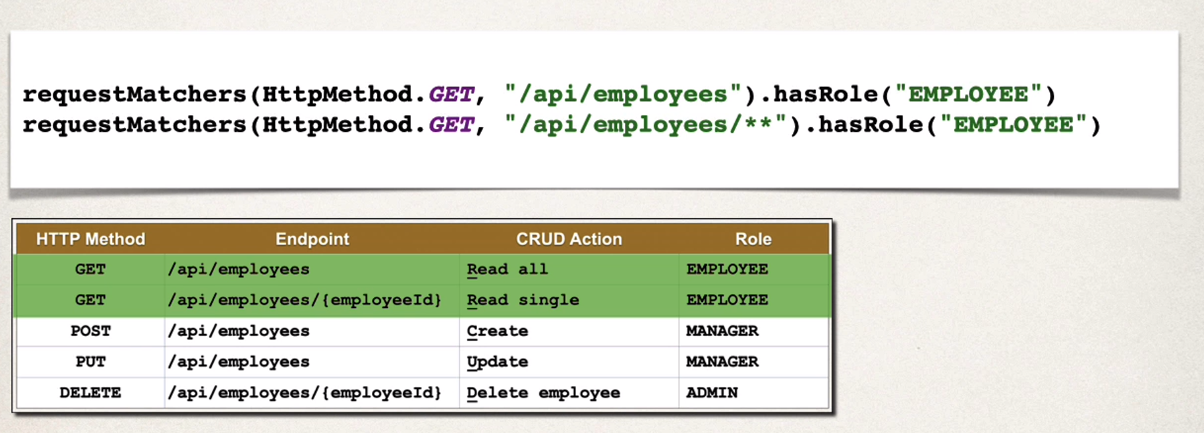
Restrict URLS based on Roles
Goal
| HTTP Method | Endpoint | CRUD action | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /api/employees | Read all | Employee |
| GET | /api/employees/{employeeID} | Read single | Employee |
| POST | /api/employees | Create | Manage |
| PUT | /api/employees | Update | Manage |
| DELETE | /api/employees/{employeeID} | Delete Employee | Admin |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception{
// configure the http requests that come in
http.authorizeHttpRequests(configure ->
configure
// employee roles
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/api/employees").hasRole("EMPLOYEE")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/api/employees/**").hasRole("EMPLOYEE")
// manager roles
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/api/employees").hasRole("MANAGER")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.PUT, "/api/employees/**").hasRole("MANAGER")
// admin roles
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.DELETE, "/api/employees/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
);
// use HTTP basic authentication
http.httpBasic(Customizer.withDefaults());
// disable csrc
// in general, not required for stateless REST APIs.
http.csrf(csrf -> csrf.disable());
return http.build();
}
Request Matchers
Security Filter Chain
DB authentication
- username and password stored in db
- we want the following users in the db just like when we had it with in memory user auth
| User ID | Password | Roles |
|---|---|---|
| john | test123 | EMPLOYEE |
| mary | test123 | EMPLOYEE, MANAGER |
| susan | test123 | EMPLOYEE, MANAGER, ADMIN |
Spring Security Database support
- jdbc auth docs
- Spring Security can read user account info from database
- By default, you have to follow Spring Security’s predefined table schemas
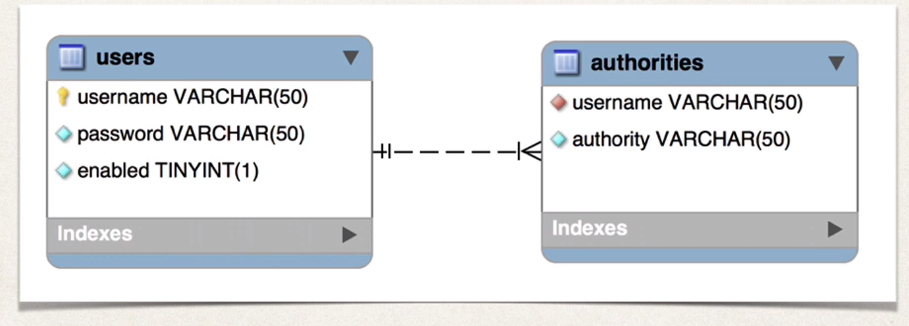
Setting up users & authorities table
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
-- Create USERS table
CREATE TABLE USERS (
USERNAME VARCHAR(128) PRIMARY KEY,
PASSWORD VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
ENABLED CHAR(1) CHECK (ENABLED IN ('Y','N')) NOT NULL
);
-- Create AUTHORITIES table
CREATE TABLE AUTHORITIES (
USERNAME VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
AUTHORITY VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT AUTHORITIES_UNIQUE UNIQUE (USERNAME, AUTHORITY),
CONSTRAINT AUTHORITIES_FK1 FOREIGN KEY (USERNAME) REFERENCES USERS (USERNAME)
);
Configuration to connect to sql tables
- comment out or remove the in memory user storage solution
1
2
3
4
5
@Bean
public UserDetailsManager userDetailsManager(DataSource datasource){
// tells Spring Security to use JDBC authentication with our data source
return new JdbcUserDetailsManager(datasource);
}
Bcrypt implementation
- No need to configure any java code, we just need to input the new bcrypt hash into the password fields of the users table records
- you may need to adjust the size of the password field to 68 chars because that is what is required for bcrypt hashes
- {bcrypt} - 8 char
- encoded password - 60 chars
- java just looks at what is inside the {} to determine what to do
- ex {noop}test123 – says that this is a plain text password
- ex {bcrypt} – says that it is a password that is hashed
Custom tables
- if we have custom authentication tables we can do the following
- in this case we have the two tables named members and roles
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
@Bean
public UserDetailsManager userDetailsManager(DataSource datasource){
JdbcUserDetailsManager jdbcUserDetailsManager = new JdbcUserDetailsManager(datasource);
// define query to retrieve a user by username
jdbcUserDetailsManager.setUsersByUsernameQuery(
"select user_id, pw, active from members where user_id=?"
);
// define query to retrieve the authorities/roles by username
jdbcUserDetailsManager.setAuthoritiesByUsernameQuery(
"select user_id, role from roles where user_id=?"
);
return jdbcUserDetailsManager;
}
Implement Spring Boot REST Security with JPA Hibernate tutorial
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.