Specialized Component annotations
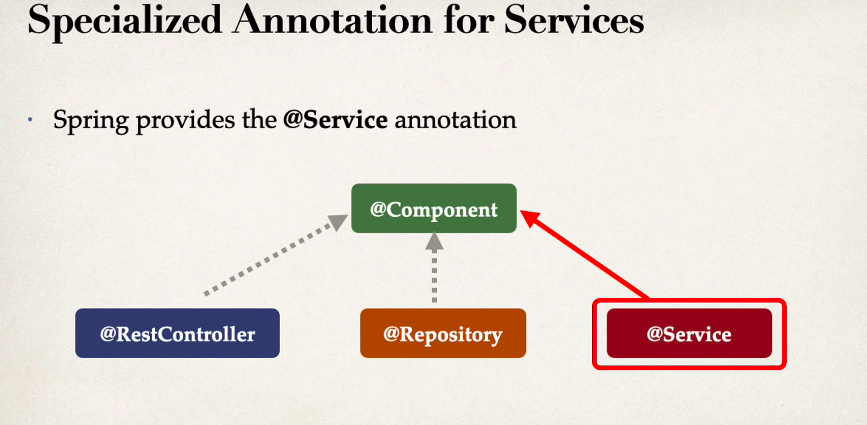
- Spring has provided a few specialized stereotype annotations: @Controller, @Service and @Repository. They all provide the same function as @Component.
- They all act the same because they are all composed annotations with @Component as a meta-annotation for each of them. They are like @Component aliases with specialized uses and meaning outside Spring auto-detection or dependency injection.
Github repo for this section
Github repo
References
@RestController, @RequestMapping & @GetMapping
- @RestController tells spring it is a rest controller class which will hold the endpoints in the class
- @RequestMapping tells spring the route for all of the sub method which will be under it
- @GetMapping tells spring this method is a GET endpoint
Sample endpoint /test/hi
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class MyControllerClass {
@GetMapping("/hi")
public String hiMethod(){
return "you've reached the /test/hi endpoint";
}
}
|
Why have a service layer
- The service layer is used so you can use all of the needed dao to implment some business logic
Best Practices
Best Practice to apply transactional boundaries at the service layer
- it is the service layer’s responsibility to manage transaction boundaries
- The @Transactional annotation should be in the service and not the dao
Java JSON Data binding
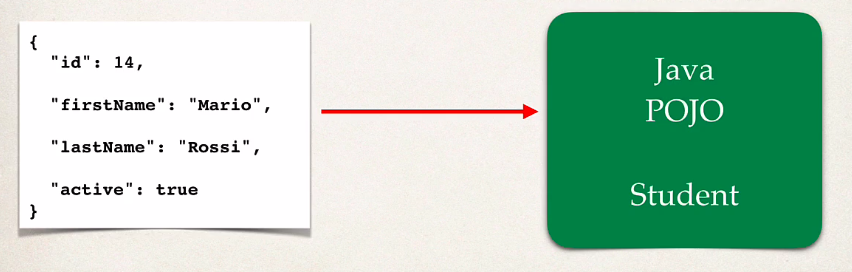
- java json binding is the process of converting JSON data to a java POJO and vice versa
- AKA
- Mapping
- Serialization / Deserialization
- Marshalling / Unmarshalling
- Spring uses the Jackson Project behind the scenes
- Convert JSON to POJO –> jackson calls setter methods
- Convert POJO to JSON –> jackson calls getter methods
- By default Jackson will call the appropiate getter / setter methods
- Java POJO must have getter and setter methods
@PathVariable
- The get mapping will have a variable placed between curly braces{}
- @PathVariable is placed before the parameters
- the variable in the {} and specified in the parameters MUST BE IDENTICAL
1
2
3
4
| @GetMapping("/student/{studentId}")
public Student getStudent(@PathVariable int studentId){
// implmenetation
}
|
Exception handling
Controller specific
@ExceptionHandler - goes above the exception handler method - Controller specific - returns a ResonseEntity which is just a http wrapped response
POJO what will be converted to JSON when returned to the caller
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public class StudentErrorReponse {
private int status;
private String message;
private long timeStamp;
// constructors
// getters and setters
}
|
Custom Exception
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class StudentNotFoundException extends RuntimeException{
public StudentNotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
// other constructors
}
|
Controller class where the top endpoint throws an exception if an invalid studentId is passed. The second method is the @ExceptionHandler where if any StudentNotFoundExceptions are thrown it will handle it according to the method body. The last method is to handle generic exceptions that are thrown
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| @GetMapping("/student/{studentId}")
public Student getStudent(@PathVariable int studentId){
if(studentId < 0 || studentId >= students.size()){
throw new StudentNotFoundException("Student with id: " +studentId + " was not found");
}
return students.get(studentId);
}
// StudentNotFoundExceptions
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<StudentErrorReponse> handleException(StudentNotFoundException studentNotFoundException){
StudentErrorReponse studentErrorReponse = new StudentErrorReponse(
404,
studentNotFoundException.getMessage(),
System.currentTimeMillis());
return new ResponseEntity<>(studentErrorReponse, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
// Generic exceptions
@ExceptionHandler ResponseEntity<StudentErrorReponse> genericException(Exception exception){
StudentErrorReponse studentErrorReponse = new StudentErrorReponse(
HttpStatus.I_AM_A_TEAPOT.value(),
"something bad generic happened",
System.currentTimeMillis()
);
return new ResponseEntity<>(studentErrorReponse, HttpStatus.I_AM_A_TEAPOT);
}
|
Global handling
- the controller specific exception handlers are great but not able to be used outside of that specific class
@ControllerAdvice
- goes above a class declaration
- like a interceptor / filter
- pre-processes requests to controllers
- post-process responses to handle exceptions
- perfect for global handling
- No other configuration is needed to tell the controllers to use these exception handlers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| @ControllerAdvice
public class StudentRestExceptionHandler {
// StudentNotFound exceptions
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<StudentErrorReponse> handleException(StudentNotFoundException studentNotFoundException){
StudentErrorReponse studentErrorReponse = new StudentErrorReponse(
404,
studentNotFoundException.getMessage(),
System.currentTimeMillis());
return new ResponseEntity<>(studentErrorReponse, HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
// Generic exceptions
@ExceptionHandler
public ResponseEntity<StudentErrorReponse> genericException(Exception exception){
StudentErrorReponse studentErrorReponse = new StudentErrorReponse(
HttpStatus.I_AM_A_TEAPOT.value(),
exception.getMessage(),
System.currentTimeMillis()
);
return new ResponseEntity<>(studentErrorReponse, HttpStatus.I_AM_A_TEAPOT);
}
}
|
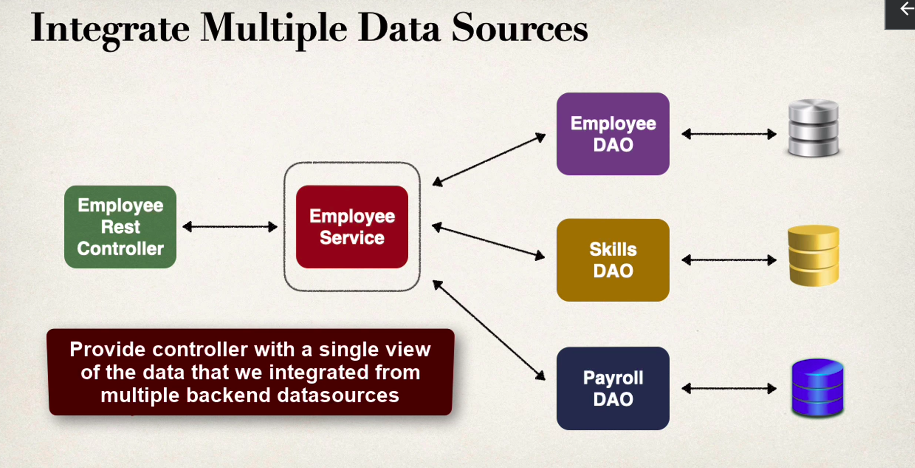
Employee Example API
Requirements
- Create a REST Api for employee directory
- Rest clients should be able to
- get a list of employees
- get a single employee
- add a new employee
- update an employee
- delete an employee
Endpoints
| HTTP Method | Endpoint | Description |
|---|
| GET | /api/employees | get all employees |
| GET | /api/employees/{employee_id} | get a single employee |
| POST | /api/employees | insert a new employee |
| PUT | /api/employees/{employee_id} | update a employee |
| DELETE | /api/employees/{employee_id} | remove a employee |
Model / Entity
This class represents the employee table in the database
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| @Entity
@Table(name = "employee")
public class Employee {
// fields
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String first_name;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String last_name;
@Column(name = "email")
private String email;
// constructors
// tostring
// getters and setters
}
|
DAO interface
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public interface EmployeeDao {
List<Employee> findAll();
Employee findById(int id);
Employee save(Employee employee);
Employee deleteById(int id);
}
|
DAO implementation
the DAO implementation uses the EntityManager that is created automatically by the spring container with all of the settings that were setup in the application.properties file.
- The enity manager has all of the methods needed to interact with the Employee database
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| @Repository
public class EmployeeDaoImpl implements EmployeeDao{
private EntityManager entityManager;
@Autowired
public EmployeeDaoImpl(EntityManager entityManager) {
this.entityManager = entityManager;
}
@Override
public List<Employee> findAll() {
// get all of the employees from the db
TypedQuery<Employee> typedQuery = entityManager.createQuery("from Employee", Employee.class);
return typedQuery.getResultList();
}
@Override
public Employee findById(int id) {
return entityManager.find(Employee.class, id);
}
@Override
public Employee save(Employee employee) {
entityManager.merge(employee);
return employee;
}
@Override
public Employee deleteById(int id) {
Employee employee = entityManager.find(Employee.class, id);
entityManager.remove(employee);
return employee;
}
}
|
Service
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public interface EmployeeService {
List<Employee> findAll();
Employee findById(int id);
Employee save(Employee employee);
Employee deleteById(int id);
}
|
Service implementation
What is the service used for
- The service is used for the business logic with the employee table
- if there were multiple daos it would inject it into the constructor dependency and be utilitzed
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| @Service
@Transactional // all methods will be wrapped in a transaction
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService{
private EmployeeDaoImpl employeeDao;
@Autowired
public EmployeeServiceImpl(EmployeeDaoImpl employeeDao) {
this.employeeDao = employeeDao;
}
@Override
public List<Employee> findAll() {
return employeeDao.findAll();
}
@Override
public Employee findById(int id) {
return employeeDao.findById(id);
}
@Override
public Employee save(Employee employee) {
return employeeDao.save(employee);
}
@Override
public Employee deleteById(int id) {
return employeeDao.deleteById(id);
}
}
|
Rest controller
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class EmployeeController {
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Autowired
public EmployeeController(EmployeeService employeeService) {
this.employeeService = employeeService;
}
// get all employees
@GetMapping("/employees")
public List<Employee> findAll(){
return employeeService.findAll();
}
// get a single employee by id
@GetMapping("/employees/{employee_id}")
public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable int employee_id){
Employee employee = employeeService.findById(employee_id);
if(employee == null){
throw new RuntimeException("Employee id not found - " + employee_id);
}
return employee;
}
// insert a new employee
@PostMapping("/employees")
public Employee addEmployee(@RequestBody Employee employee){
employee.setId(0);
Employee dbEmployee = employeeService.save(employee);
return dbEmployee;
}
// updates an employee or adds it if not in the db
@PutMapping("/employees/{employee_id}")
public Employee updateEmployee(@RequestBody Employee employee, @PathVariable int employee_id){
// the id does not exist
if(employeeService.findById(employee_id) == null){
throw new RuntimeException("No employee with id: " +employee_id + " was found");
}
employee.setId(employee_id);
employeeService.save(employee);
return employee;
}
// delete an employee by id
@DeleteMapping("/employees/{employee_id}")
public Employee deleteEmployee(@PathVariable int employee_id){
if(employeeService.findById(employee_id) == null){
throw new RuntimeException("Employee with id: " + employee_id + " was not found...");
}
return employeeService.deleteById(employee_id);
}
}
|
Creating the CRUD DAO automatically by spring instead of creating different DAO for different entities
- This is achieved by using Spring Data JPA
- You create a DAO by just plugging in your entity type and primary key
- Spring will give you a CRUD implmenentaton for free instead of having to create a DAO interface and DAO implementation for every entity like the example above
JPARepository
- Spring Data JPA provides the interface JpaRepository
- Exposes methods
- findAll()
- findById()
- save()
- deleteById()
- others…
- All you have to do is extend the JpaRepository and you get all of the implmemented methods for free!
- Works by using generics
- JpaRepository<Entity, PrimaryKey>
- Provides the @Transactional so you don’t have to specify in the service class
1
2
3
| public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> {
// that's it, no need to write code!!!
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public interface EmployeeService {
Employee save(Employee employee);
List<Employee> findAll();
Employee findById(int id);
Employee removeById(int id);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| @Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService{
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@Autowired
public EmployeeServiceImpl(EmployeeRepository employeeRepository) {
this.employeeRepository = employeeRepository;
}
@Override
public Employee save(Employee employee) {
return employeeRepository.save(employee);
}
@Override
public List<Employee> findAll() {
return employeeRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public Employee findById(int id) {
if(employeeRepository.findById(id).isPresent()){
return employeeRepository.findById(id).get();
}
else{
return null;
}
}
@Override
public Employee removeById(int id) {
Optional<Employee> employee = employeeRepository.findById(id);
if(employee.isPresent()){
employeeRepository.deleteById(id);
return employee.get();
}
return null;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| @RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class Controller {
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Autowired
public Controller(EmployeeService employeeService) {
this.employeeService = employeeService;
}
// get all employees
@GetMapping("/employees")
public List<Employee> getEmployees(){
return employeeService.findAll();
}
// get single employee
@GetMapping("/employees/{employee_id}")
public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable int employee_id){
Employee employee = employeeService.findById(employee_id);
if(employee == null){
throw new RuntimeException("No employee with id: " +employee_id +" was found");
}
return employee;
}
// add new employee
@PostMapping("/employees")
public Employee newEmployee(@RequestBody Employee employee){
return employeeService.save(employee);
}
// update single employee
@PutMapping("/employees/{employee_id}")
public Employee newEmployee(@RequestBody Employee employee, @PathVariable int employee_id){
if(employeeService.findById(employee_id) == null){
throw new RuntimeException("Employee with id: " +employee_id +" was not found...");
}
employee.setId(employee_id);
return employeeService.save(employee);
}
// delete single employee
@DeleteMapping("employees/{employee_id}")
public Employee deleteEmployee(@PathVariable int employee_id){
Employee employee = employeeService.removeById(employee_id);
if(employee == null){
throw new RuntimeException("No employee with id: " +employee_id +" was found...");
}
return employee;
}
}
|
Extended features
- you can add additonal things like
- extending and adding custom queries with JPQl
- Query Domain Specific Lanauge (Query DSL)
- Defining custom methods (low-level coding)
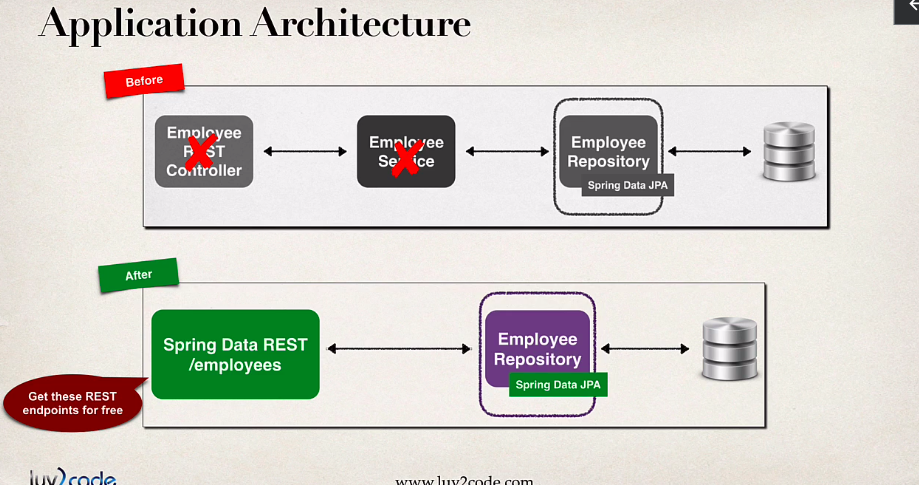
Spring Data REST
- Spring Data REST does what Spring Data Jpa does for DAO’s but for the REST controller
- leverages JpaRepository to give you a REST CRUD implementation for free
- minimizes boiler-plate REST code
Endpints exposed for you
| HTTP Method | Endpoint | CRUD Action |
|---|
| GET | /employees | Read a list of employees |
| POST | /employees | Create a new employee |
| GET | /employees/{employeeId} | Get a single employee |
| PUT | /employees/{employeeId} | Update an existing employee |
| DELETE | /employees/{employeeId} | Delete an existing employee |
How does it work
- Spring Data REST will scan your project for JpaRepository
- Expose REST APIs for each enity type for you JpaRepository
1
2
| public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> {
}
|
How do you implement this?
- All you do is have to add the dependency in the pom.xml file and add your JpaRepository entity interfaces and spring will automatically scan them and implement the CRUD API
Architectur before/after
HATEOAS compliant
- Spring Data REST endpoints are HATEOAS compliant
- HATEOAS - Hypermedia as the Engine of Application State
- think of it as meta-data for REST data
- example of hateoas compliant for a get request of a single entity
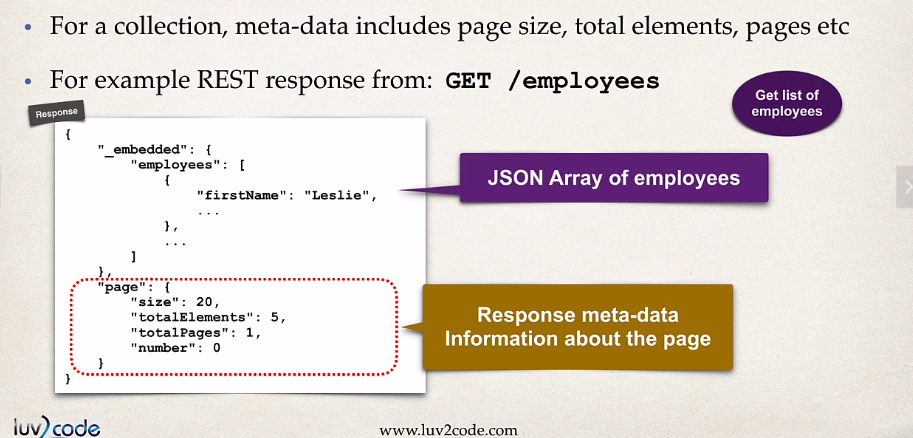
- example of hateoas compliant for a collection response which contains
- page size
- total elements
- pages, etc..
Spring Data REST Advanced Features
- Pagination, sorting and searching
Base path for the endpoints
- Can be specified in the applicaton.properties file with the following
1
| spring.data.rest.base-path=/api
|
Manually specifying plural names for the endpoints
- Done with the @RepositoryRestResource(path=”endpointname”)
1
2
3
| @RepositoryRestResource(path = "members")
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> {
}
|
Accessing different pages
- spring data-rest defaults to 20 results
- we can change that with the following appendage to the url
- Zero based
http://localhost:3000/api/memebers?page=0
Spring Data REST configurations
| Name | Description |
|---|
| spring.data.rest.base-path | Base path used to expose repository resources |
| spring.data.rest.default-page-size | Default size of pages |
| spring.data.rest.max-page-size | Maximum size of pages |
Sorting
- We can sort by maniupulating the url
- For some reason there is a bug where it won’t work if you try to sort with a field that is using underscores
- example http://localhost:8080/employees?sort=last_name – does not work
- but if you camelCase it would work with lastName
- stack overflow underscores issue sorting
- Sort by last name
- http://localhost:8080/employees?sort=last_name
- Sort by first name
- http://localhost:8080/employees?sort=last_name
- Sort first name descending
- http://localhost:8080/employees?sort=last_name, desc