Udemy Spring boot course: Section 3 Hibernate/JPA
- Git repo for this section
- Hibernate
- JPA
- Setting up Docker MySQL
- Automatic Data Source Configuratin
- Commandline app
- Entity class @Entity / @Table
- JPQL
- spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=<PROPERTY-VALUE>
- Add logs for SQL and jdbc bind
Git repo for this section
Hibernate
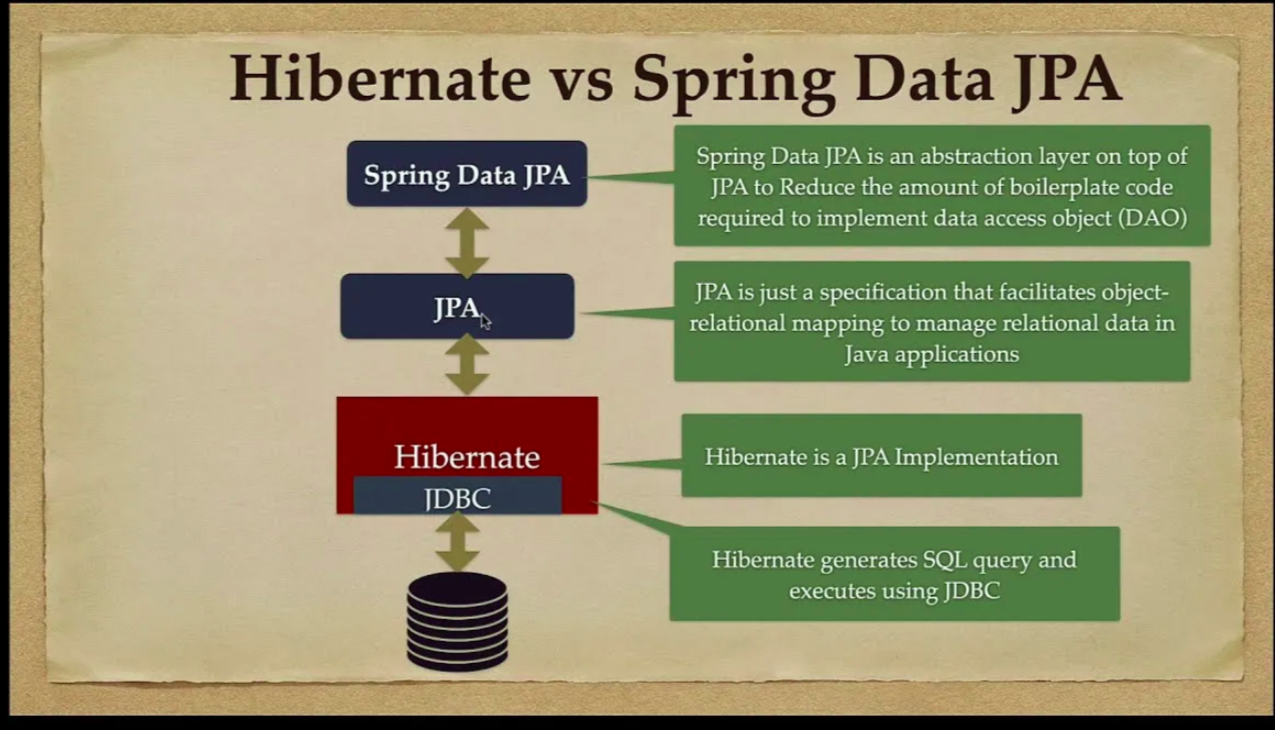
What is Hibernate
- A framework for persisting / saving java objects in a database
Benefits
- Handles all of the low-level SQL
- Minimizes the amount of JDBC code you have to develop
- Hibernate provides the Object-to-Relational Mapping (ORM)
ORM
JPA
What is JPA?
- Jakarta Persistence API (JPA)
- Standard API for ORM
- Only a Specification
JPA Vendor implementations
- Hibernate
- EclipseLink
Benefits of JPA
- Not locked into a specific vendor
- portable, flexible code by coding to JPA spec
How is JDBC related to Hibernate and JPA
- JPA uses JDBC behind the scenes
- JPA is just another layer of abstraction
Setting up Docker MySQL
- Docker hub mysql
- Steps
- Get the docker image
docker pull mysql
- Create the docker instance
docker run --name mysql-db -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root -d mysql:latest
- Connect to instance to test find the ip
mysql -h 172.17.0.3 -u root -p
- Get the docker image
Setting up Docker PhpMyAdmin
- Docker hub PhpMyAdmin
- Steps
- get the docker image
docker pull phpmyadmin
- create the docker container
docker run --name phpmyadmin -d --link mysql-db -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root -e PMA_HOST=172.17.0.3 -e PMA_PORT=3306 -p 8080:80 phpmyadmin
- Navigate to PhpMyAdmin
- 0.0.0.0:8080
- Login
- username: root
- password: root
- get the docker image
Automatic Data Source Configuratin
- Based on configs, Springboot will automatically create the beans:
- DataSource, EntityManage
DB connection
- Db connection info is read from application.properties
1
2
3
4
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://172.17.0.3:3306/student_tracker
spring.datasource.username=springstudent
spring.datasource.password=springstudent
server.port=8081
Commandline app
- Spring commandline app
- Method with @Bean annotation placed after main method
- returns CommandLineRunner
- the commandLineRunner() method is called after the application context is loaded, but before the execution of the main method is complete.
1st option, use the @Bean annotation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
@SpringBootApplication
public class CruddemoApplication {
public static void main(String[alt-text] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CruddemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(String[alt-text] args){
return run -> {
System.out.println("Hello world");
};
}
}
2nd option, have the class implement CommandLineRunner and implement the run() method
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@SpringBootApplication
public class CruddemoApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
public static void main(String[alt-text] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CruddemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Hello world");
}
}
Reduce logging level and spring banner
- Adjust the application.properties file with the following
1
2
3
4
5
# turn off the springboot bannner
spring.main.banner-mode=off
# Reduce the logging level
logging.level.root=warn
Entity class @Entity / @Table
- Java class that is mapped to a database table
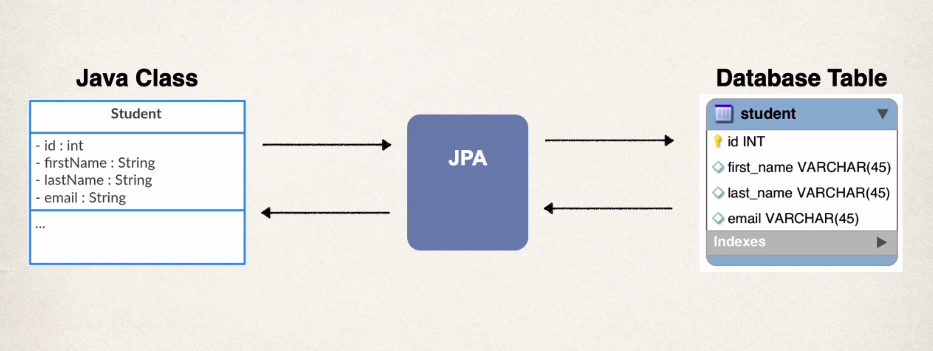
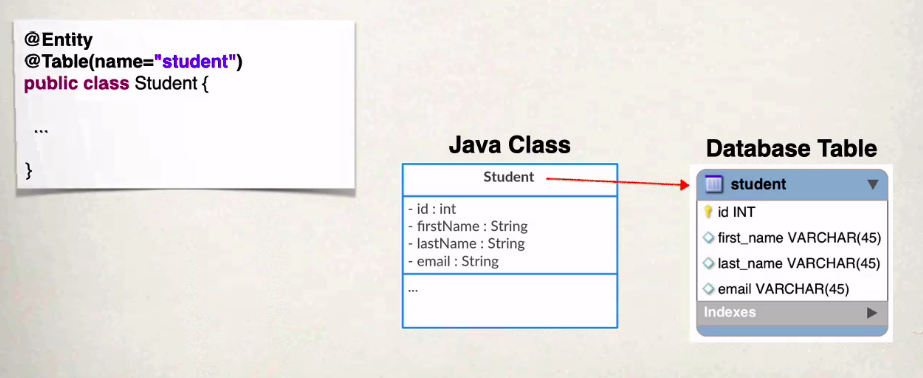
- annotated with the @Entity annotaion
- must have public or protected no-argument constructor
- class can have other constructors
- @Table(“tableName”) the name in quotes is optional
- however it is recommended that you input a table name because if you change it later on it could be a breaking change
- if not specified it will be the name of the class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
@Entity
@Table(name="student")
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
private int id;
@Column(name="first_name")
private String firstName;
}
Columns @Column
- The columns names are optional
- if not specified, the column name is the same name as the field name
- not recommended
- if you refactor field name it is not reflected in the db making it a breaking change
Generation ID Strategies
- How an id is generated
- typically for the primary key
- @GeneratedValue(GenerationType.AUTO)
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| GenerationType.AUTO | Pick an appropriate strategy for the particular database |
| GenerationType.IDENTITY | Assign primary keys using database identity column |
| GenerationType.SEQUENCE | Assign primary keys using a database sequence |
| GenerationType.TABLE | Assign primary keys using an underlying database table to ensure uniqueness |
- You can define your own CUSTOM generation strategy
- implmement the org.hibernate.id.IdentifierGenerator
- override the public Serializable generate() method
Data Access Object (DAO)
- Responsible for interfacing with the db
- Like a helper class for communicating with our db
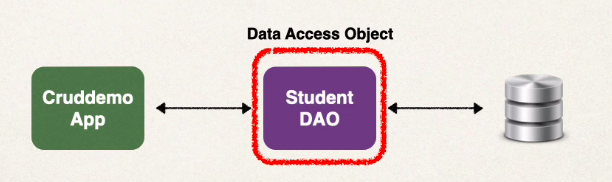
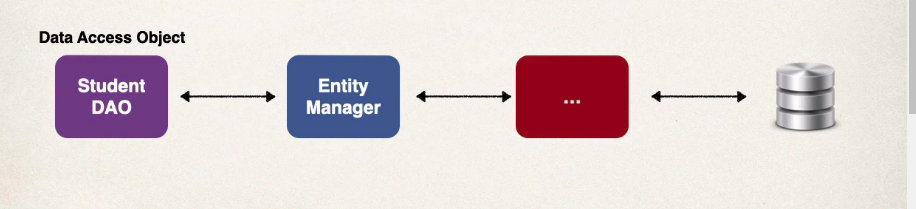
- The DAO uses the entity manager for saving/retrieving and other operations with the db
Data Access Object Methods()
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| save() | Save the object |
| findById() | find student by primary key |
| findAll() | get all of the students |
| update() | update a student record |
| delete() | delete a student record |
| deleteAll() | delete all from the table |
| findByLastName() | Finds a student by a lastname |
- like findByLastName() there will be a method for each of the fields
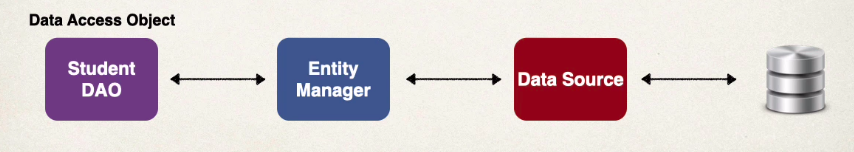
JPA Entity Manager
- In JPA, the EntityManager interface is used to allow applications to manage and search for entities in the relational database. The EntityManager is an API that manages the lifecycle of entity instances.
- JPA Entity Manager and Data source are automatically created by springboot
- based on the file application.properties
- We can autowire / inject the JPA Entity Manager into our Student DAO
Example CRUD command line app
Create the Student table with the student class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
@Entity
@Table(name="student")
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
private int id;
@Column(name="first_name")
private String firstname;
@Column(name="last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name="email")
private String email;
// empty constructor
public Student() {
}
// field constructor
public Student(String firstname, String lastName, String email) {
this.firstname = firstname;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
}
// getters and setters
}
Create the Student DAO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public interface StudentDAO {
void save(Student student);
Student findById(Integer id);
List<Student> findAll();
List<Student> findByLastName(String lastName);
void update(Student student);
Student delete(Integer id);
}
create a concrete class that implements the StudentDAO interface
- using contstructor dependency injection
- @Repository
- specialization of the @Component annotation
- support for component scanning
- Translates JDBC exceptions
- @Transactional
- the operation will be wrapped in a transaction
- The EntityManager object is created automatically by spring with the credentials specified in application.properties file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
@Repository
public class StudentDAOImpl implements StudentDAO{
// define field for entity manager
private EntityManager entityManager;
// inject entity manager using constructor injection
@Autowired
public StudentDAOImpl(EntityManager entityManager) {
this.entityManager = entityManager;
}
@Override
@Transactional
public void save(Student student) {
entityManager.persist(student); // saves the student in the db
}
@Override
public Student findById(Integer id) {
return entityManager.find(Student.class, id);
}
@Override
public List<Student> findAll() {
TypedQuery<Student> typedQuery = entityManager.createQuery(
"FROM Student", Student.class);
return typedQuery.getResultList();
}
@Override
public List<Student> findByLastName(String lastName) {
TypedQuery<Student> typedQuery = entityManager.createQuery(
"FROM Student WHERE lastName = :variable",
Student.class
);
typedQuery.setParameter("variable", lastName);
return typedQuery.getResultList();
}
@Override
@Transactional
public void update(Student student) {
// this updates the student
entityManager.merge(student);
}
@Override
@Transactional
public Student delete(Integer id) {
// gets the student from the db
Student student = this.findById(id);
// student not found
if(student == null){
return null;
}
// delete from the db
entityManager.remove(student);
// return the student
return student;
}
}
Here is the main method and commandLineRunner methods()
- the StudentDAO is injected by spring and the lambda expression is ran
- createStudent takes in the studentDAO and creates a student
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
@SpringBootApplication
public class CruddemoApplication {
public static void main(String[alt-text] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CruddemoApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner(StudentDAO studentDAO){
return runner -> {
// createStudent(studentDAO);
// readStudent(studentDAO);
// getStudents(studentDAO);
// findStudentByLastname(studentDAO);
// updateStudent(studentDAO);
deleteStudent(studentDAO);
};
}
// CREATE
private void createStudent(StudentDAO studentDAO) {
// create the student object
System.out.println("Creating the student...");
Student student = new Student("jordan", "Sinatra", "jordanSin@gmail.com");
// save the student
System.out.println("Saving the student...");
studentDAO.save(student);
// display id of the saved student
System.out.println("Student id: " + student.getId());
}
// READ
private void readStudent(StudentDAO studentDAO){
int id = 12;
Student student = studentDAO.findById(id);
if(student != null){
System.out.println(student);
}
else {
System.out.println("Unable to find student with id: " +id);
}
}
private void getStudents(StudentDAO studentDAO){
List<Student> students = studentDAO.findAll();
for(var student : students){
System.out.println(student);
}
}
private void findStudentByLastname(StudentDAO studentDAO){
String lastName = "Sinatra";
List<Student> students = studentDAO.findByLastName(lastName);
for(var student : students){
System.out.println(student);
}
}
// UPDATE
private void updateStudent(StudentDAO studentDAO){
Student student = studentDAO.findById(1);
student.setFirstname("Tristan");
studentDAO.update(student);
System.out.println("updated student: ");
System.out.println(student);
}
// DELETE
private void deleteStudent(StudentDAO studentDAO){
int id = 5;
Student student = studentDAO.delete(id);
if(student == null){
System.out.println("no student was found with id: " + id);
}
else{
System.out.println("removed student: ");
System.out.println(student);
}
}
}
JPQL
- JPA Query Language for doing things like querying objects
- similiar to SQL
- where, like, order by, join, in, etc…
- Based on entity name and entity fields
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=<PROPERTY-VALUE>
- If we wanted hibernate to create tables if they are not already created we have to add the following to the application.properties file
- No further configuration to the @Entity class
1
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create
Here are some other Property values to choose from:
| Property Value | Description |
|---|---|
| none | No action will be performed |
| create-only | Database tables are only created |
| drop | Database tables are dropped |
| create | Database tables are dropped, followed by database tables creation |
| create-drop | Database tables are dropped followed by database tables creation. On application shutdown, drope the database tables |
| validate | Validate the database tables schema |
| update | Update the database tables schema |
Add logs for SQL and jdbc bind
- Add logs to the terminal for SQL Queries made by the orm
1
2
logging.level.org.hibernate.SQL=debug
logging.level.org.hibernate.orm.jdbc.bind=trace
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.