Udemy Spring boot course: Section 1 QuickStart
- Overview
- Github repo
- Spring boot version
- Standard Directory Structure
- Spring Framework
- Springboot Framework
- What is it?
- Spring and Springboot
- Spring Initializr
- Springboot Starters
- Springboot embedded server
- Running a Springboot application
- Enable Auto-reload for Spring project
- Deploying Springboot applications
- Does Springboot replace Spring MVC, Spring Core, Spring AOP, Spring REST, Spring….
- Does Springboot run faster than regular Spring code?
- Spring Projects
- Springboot Actuator
- Springboot Actuator Security
- Maven
- Creating a demo springboot application
- Configure app to read from Application Properties file
- Common Springboot application properties
Overview
Github repo
Spring boot version
- Using Spring boot 3
- requires JDK 17 or higher
Standard Directory Structure
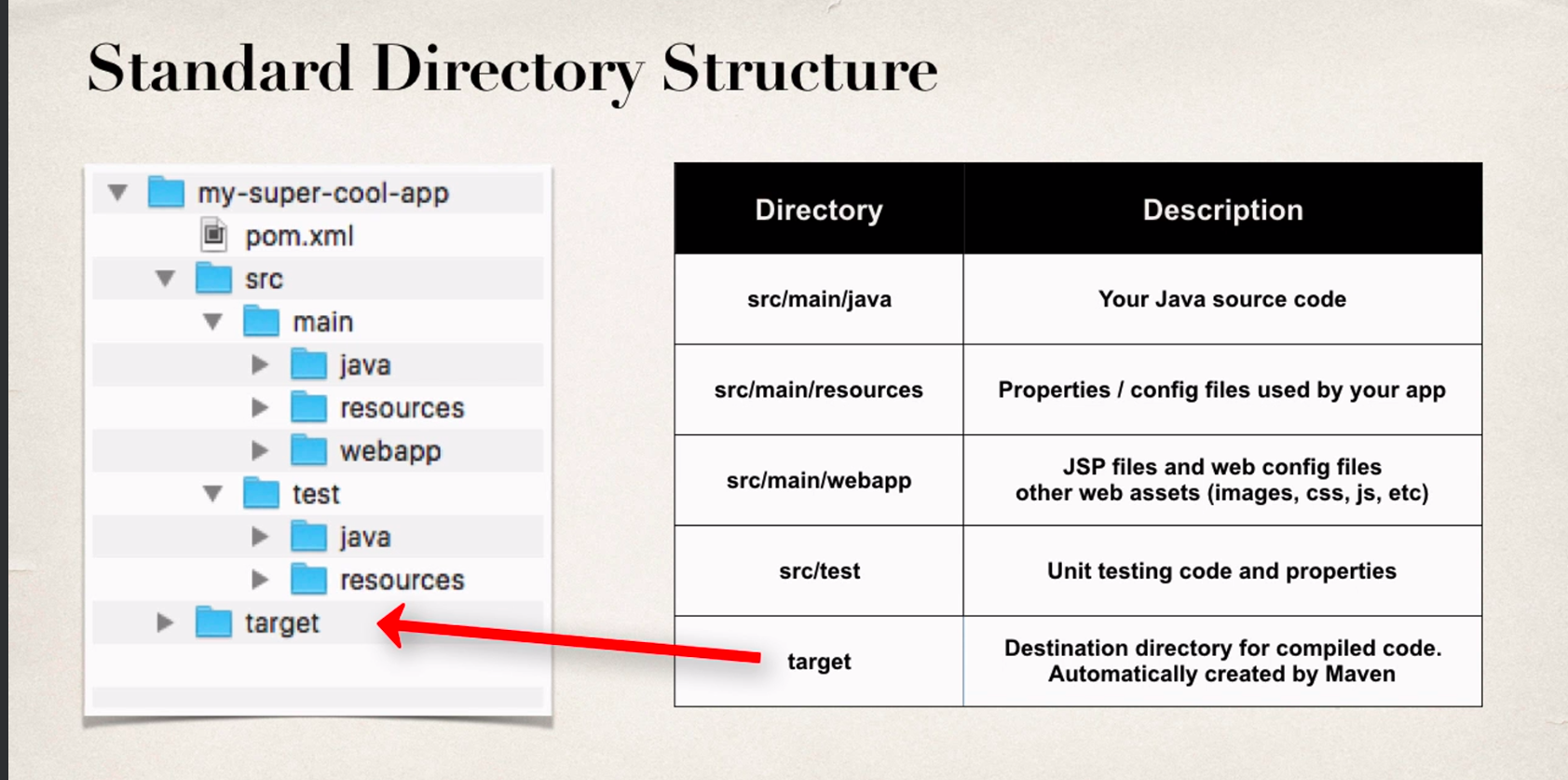
- if doing a web app place the webapp files in src>main>webapp

- By default Spring boot will load properties from: application.properties
- things like where the port number can be configured
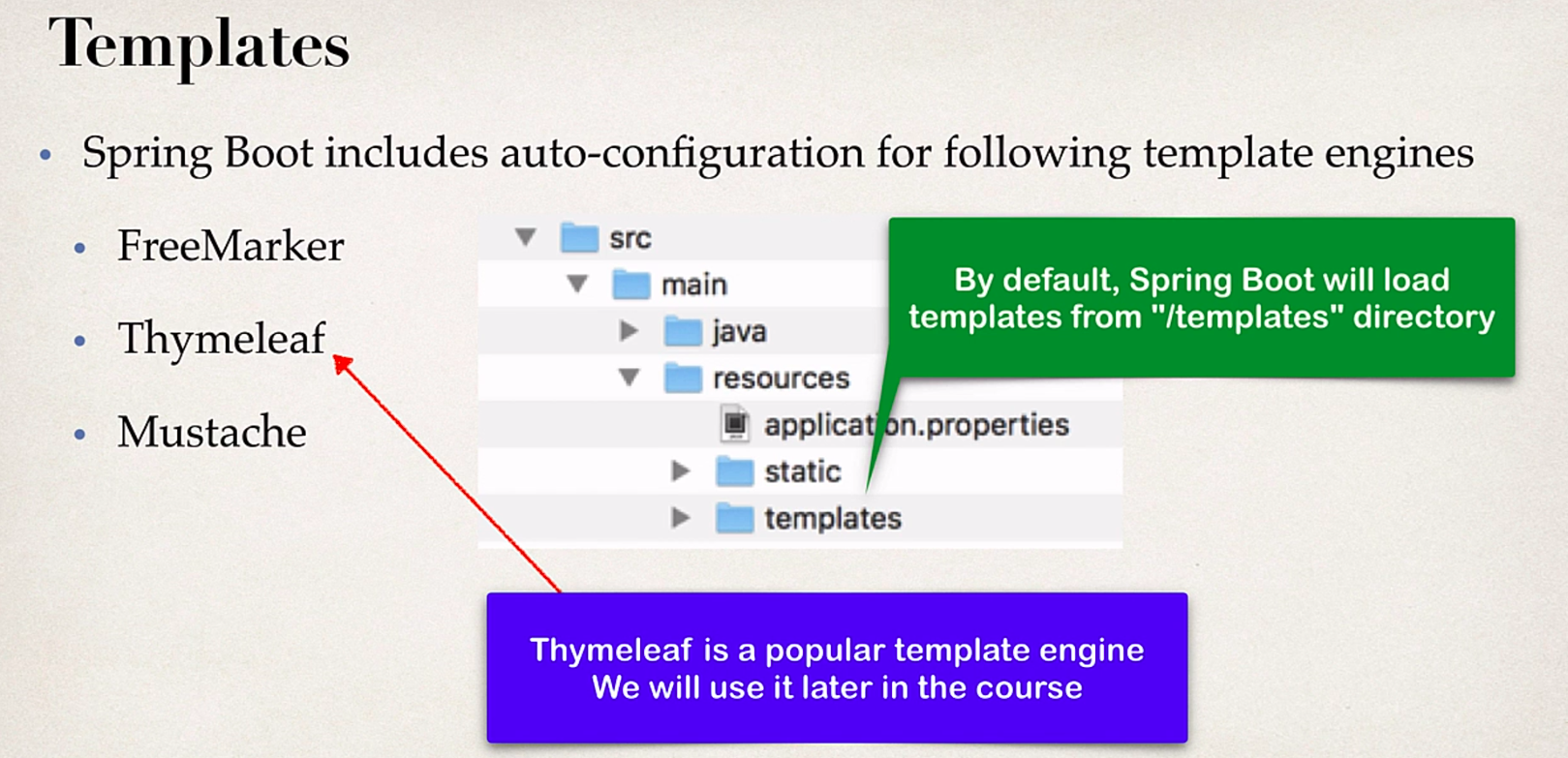
Spring Framework
- Lightweight dev with Java POJOs
- Dependency injection to promote loose coupling
Overview
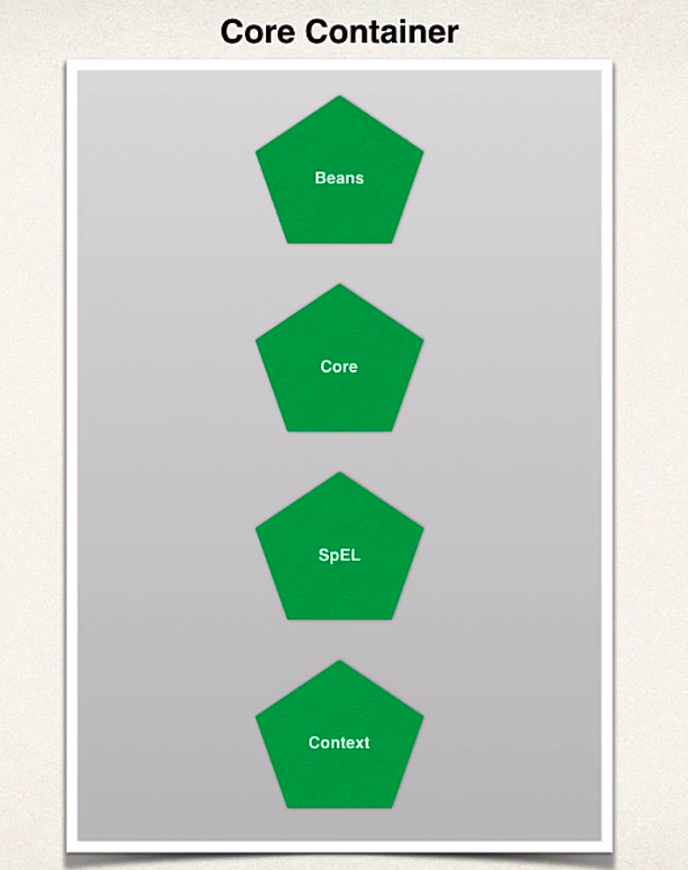
- the core container is the heart of spring
- it manages how beans are created
- it has a bean factory for creating beans
- SpEL - Spring expression language: language in the config files to refer to other beans
Springboot Framework
What is it?
- popular framework for building java applications
- provides a large number of helper classes and annnotations
- Normal Spring applications take a lot of effort just to get setup
- Springboot is the solution to that making it easier and faster to get started with Spring development
- minimizes the amount of manual configuration
- performs auto-configuration based on props files and JAR classpath
- provides an embedded HTTP server so you can get started quickly
- Tomcat, jetty, undertow
Spring and Springboot
- Springboot uses spring behind the scenes
- Springboot simply makes it easier to use Spring
Spring Initializr
- start.spring.io
- Site to quickly create a starter spring boot project
- select your dependencies
- then creates a Maven / Gradle project
- then import the project into your ide
Springboot Starters
- Curated list of maven dependencies
- A collction of dependencies grouped together
- Example:
- Spring-boot-starter-web
- list of spring boot starters
Springboot embedded server

- springboot provides an embedded HTTP server so you can get started quickly
- Tomcat, Jetty, Undertow
- self contained unit in the .jar file. nothing else you have to install!!
Running a Springboot application
- Since everything is self contained in the .jar file
- We can run the springboot application with
java -jar mycoolapp.jar- runs the app and spins up the server!
- spring boot maven plugin option
- You can also run the application by running
mvn spring-boot:runor using the mvnw.sh file./mvnw spring-boot:run
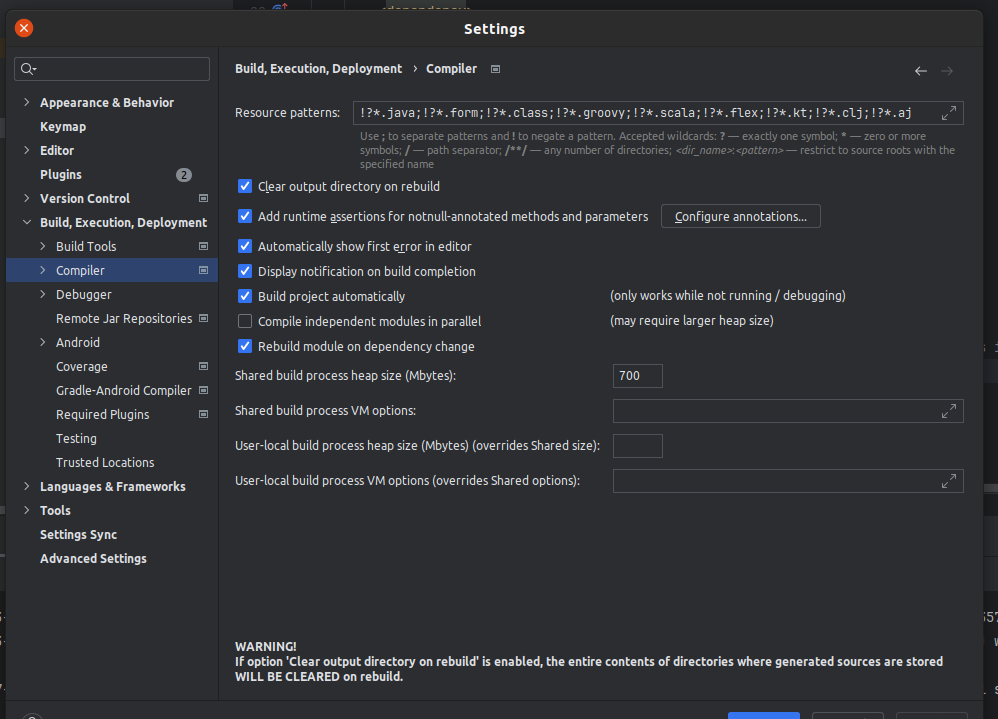
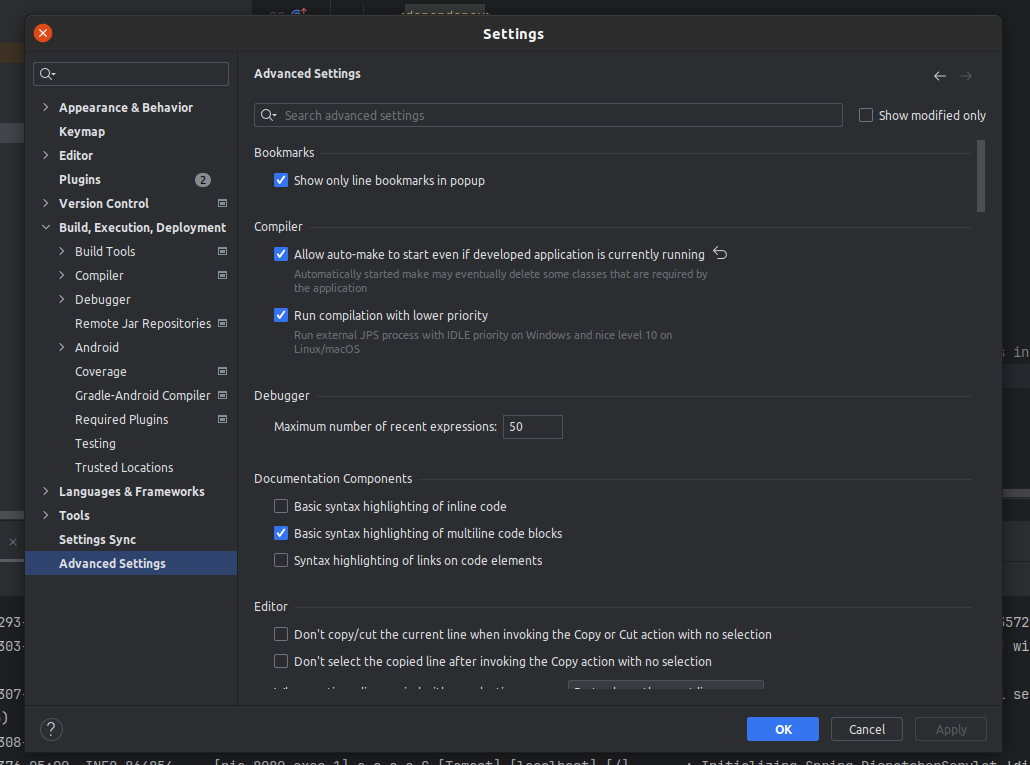
Enable Auto-reload for Spring project
- You can enable auto-reloading for a spring project so you don’t have to stop and start all the time to see the changes
- You have to run from intellij run logo, won’t work if you run from the terminal with
./mvnw spring-boot:run - Place the dependency in the pom.xml file
1
2
3
4
5
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional> <!-- Can prevent passing devtools dependencies into other modules -->
</dependency>
- Enable “Build Project Automatically”
- Enable “Allow auto-make to start even if developed application is currently running”
Deploying Springboot applications

- Springboot apps can also be deployed in the traditional way with WAR files
- Deploy WAR file to an external server: Tomcat, JBoss, WebSpher
- Do not use the src/main/webapp directory if app is packaged as a WAR
- Although standard convention by maven, it works only with WAR packaging
- it is silently ignored by most build tools if you generate a JAR
Does Springboot replace Spring MVC, Spring Core, Spring AOP, Spring REST, Spring….
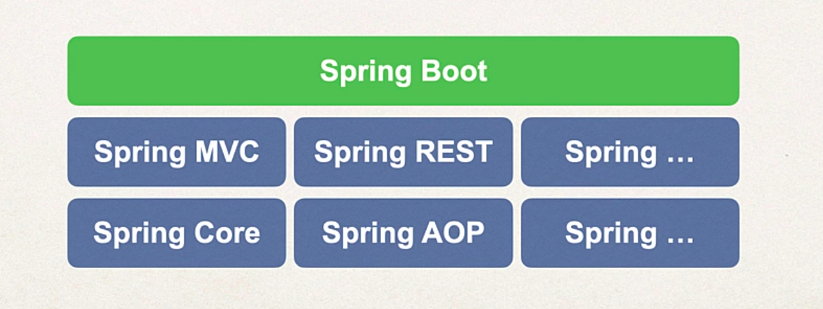
- No Springboot does not replace but rather uses them behind the scenes abstracting the manual config away from the user
Does Springboot run faster than regular Spring code?
- No, it uses the same code of the Spring framework
Spring Projects
- Spring projects are additional Spring modules built-on top of the Spring Framework
- Spring Cloud, Spring Data, Spring Batch, Spring Security .. .
- spring projects site
Springboot Actuator
- Exposes endpoints to monitor and manage springboot application
- dev-ops functionality out of the box
- Just add the following dependency to your pom.xml file and REST endpoints are automatically added to your application
1
2
3
4
5
<dependency>
<version>3.1.3</version>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
To get access to the /actuator/info we need to add the following lines to the application.properties file
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# Enabling the /health & /info endpoints only
#management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=health,info
# Expose all endpoints with the wildcard
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
# Customizing the /actuator/info endpoint
management.info.env.enabled=true # tells the plugin to read the variables below to display on the /info route
info.app.name=Hello world App
info.app.description=Demo Spring Boot app
info.app.version=1.0
| Endpoint | Description |
|---|---|
| /actuator/health | Health of the application |
| /actuator/info | information of the application |
| /actuator/auditevents | Audit events for your app |
| /actuator/beans | list of all of the beans registered in the Spring application context |
| /actuator/mappings | list of all @Requestmapping paths |
Springboot Actuator Security
- You may want to add security so everyone doesn’t have access to the actuator endpoints
1
2
3
4
5
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
<version>3.1.4</version>
</dependency>
- After adding the plugin, spring security will prompt for a login
- Default user –> user
- Default password –> Generated by the console
- There are more advanced ways to configure spring security like connecting to a db but for now we will just use the method below
- If you want to override the defaults you can specify the credentials in the application.properties like below
1
2
spring.security.user.name=tresten
spring.security.user.password=password123
Maven
What is Maven
- When building your java project, you may need additional JAR files
- ex. Spring, Hibernate, Commong Logging
- One approach is to download the JAR files from each project web site
- Manually add the JAR files to your build / classpath
- Instead
- All you do is have to tell maven what dependencies you will need
- Maven will go out and download the JAR files for those projects for you
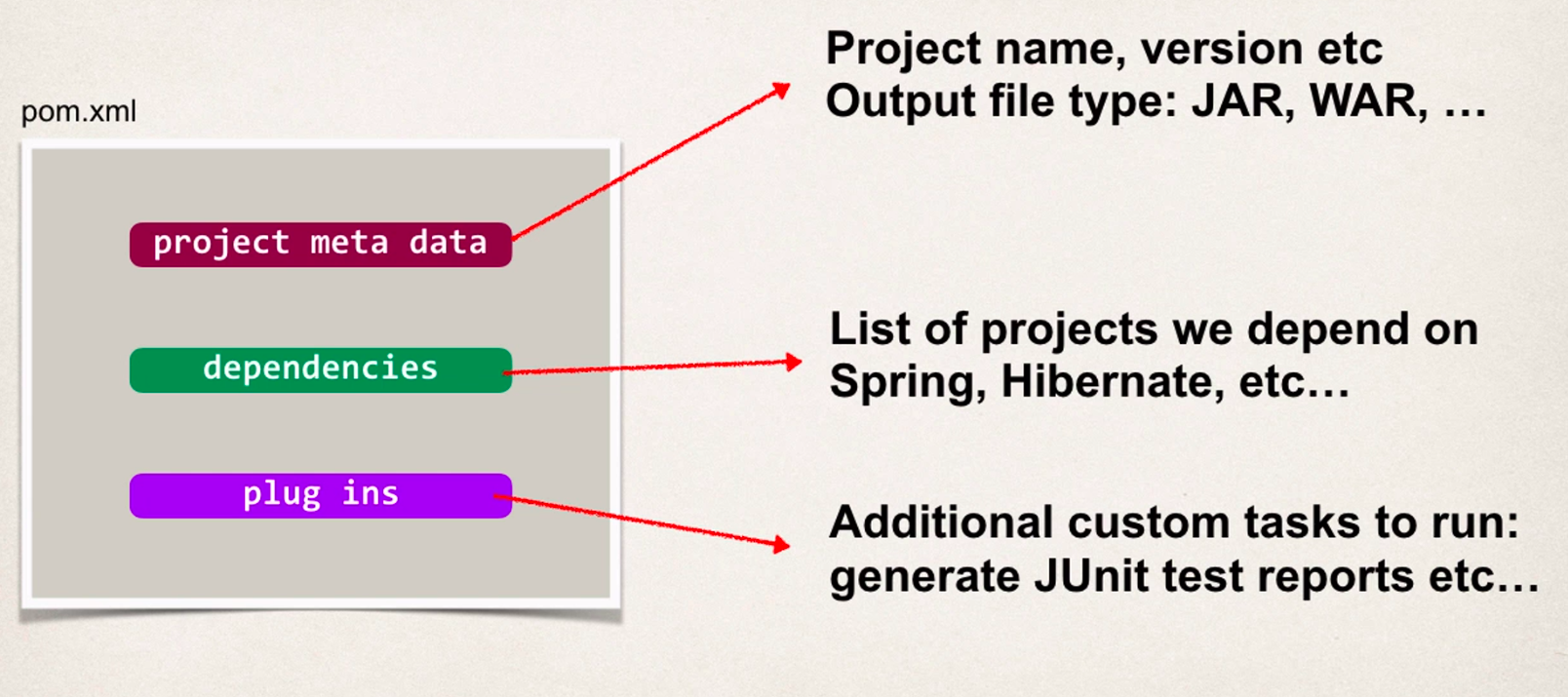
POM file
Project Coordinates
- where maven goes to look to download

- referred to as GAV (Group ID, Artificat ID, Version)
- maven search
mvnw
- mvnw allows you to run a Maven project
- no need to have maven installed
- if maven installed is not correct version it will automatically update it to the latest version
- two mvn files for windows or linux/mac
- mvnw.cmd – windows
- mvnw.sh – linux/mac
Maven Errors
- JDK17 does not work with mvn 3.6.0 error fix
- I was getting warning error when attempting to run
mvn packageormvn spring-boot:runsaying Java_Home was not set- I had placed the following lines in
/etc/environmentas root
- I had placed the following lines in
1
2
JAVA_HOME="/usr/lib/jvm/jdk-17-oracle-x64"
export JAVA_HOME
- After the modification run
source /etc/environment
Maven Commands
- Cheat sheet
- Creates the target/ directory with all necessary file and the .jar file
1
./mvnw package
- Deletes all in target/ directory and removes the directory
1
./mvnw clean
- Run the spring boot application with the maven spring boot plugin
1
./mvnw spring-boot:run
Creating a demo springboot application
Steps
Spring initializer
- go to the spring initializer site
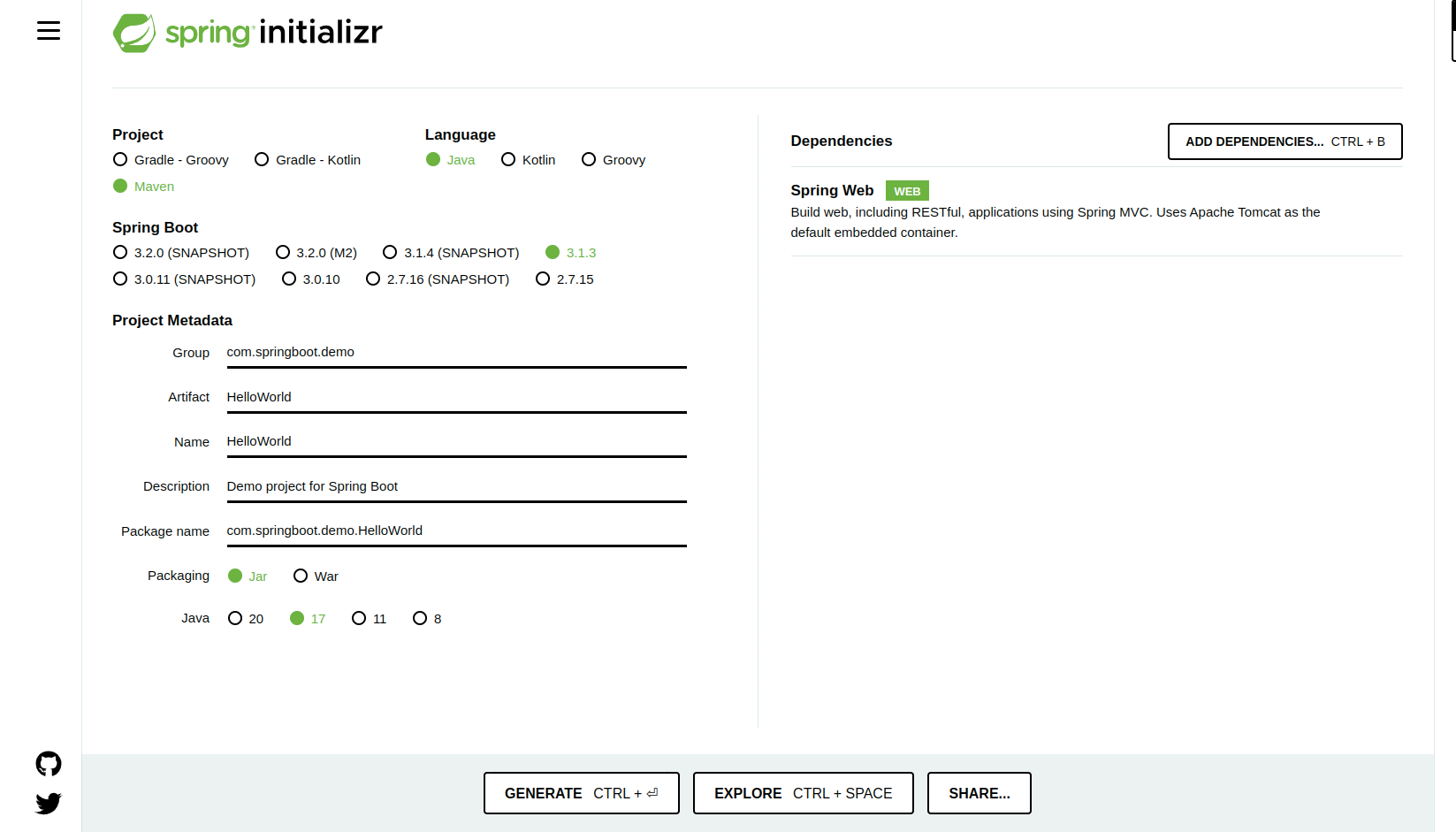
- enter out the project information
- add the dependencies on the right, (selected spring web for this demo)
- hit generate, download the file, unzip to a directory and open up in ide
Run the app
- Go to the main method and hit the run button
- next you will see the following code in the terminal output
1
2
3
4
5
6
2023-09-19T16:21:21.693-05:00 INFO 741662 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardService : Starting service [Tomcat]
2023-09-19T16:21:21.693-05:00 INFO 741662 --- [ main] o.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngine : Starting Servlet engine: [Apache Tomcat/10.1.12]
2023-09-19T16:21:21.792-05:00 INFO 741662 --- [ main] o.a.c.c.C.[Tomcat].[localhost].[/] : Initializing Spring embedded WebApplicationContext
2023-09-19T16:21:21.793-05:00 INFO 741662 --- [ main] w.s.c.ServletWebServerApplicationContext : Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in 1020 ms
2023-09-19T16:21:22.146-05:00 INFO 741662 --- [ main] o.s.b.w.embedded.tomcat.TomcatWebServer : Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http) with context path ''
2023-09-19T16:21:22.155-05:00 INFO 741662 --- [ main] c.s.d.HelloWorld.HelloWorldApplication : Started HelloWorldApplication in 1.908 seconds (process running for 2.26)
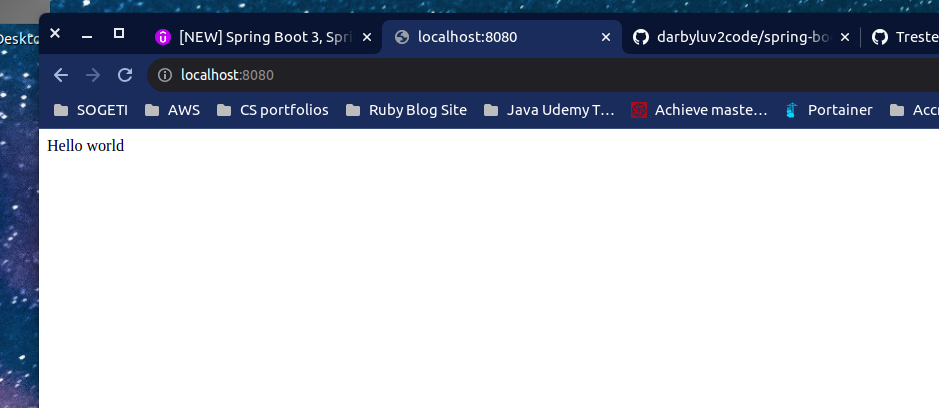
- However when we attempt to go to the site at localhost:8080 we get this error because we have no routes setup
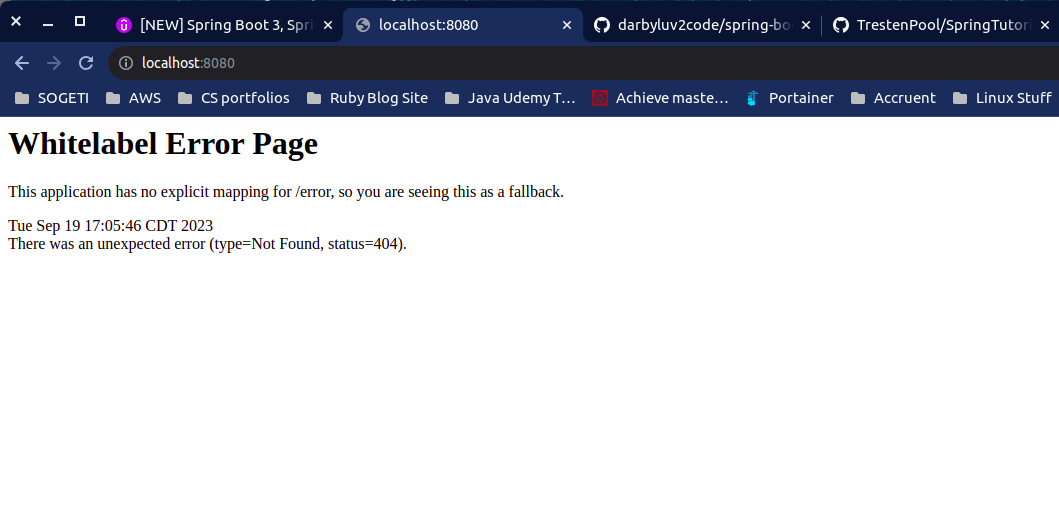
Setup / mapping
- We will setup a mapping for the “/” endpoint
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
package com.springboot.demo.HelloWorld.rest;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class FunRestController {
// expose "/" that return "Hello world"
@GetMapping("/")
public String sayHello(){
return "Hello world";
}
}
Configure app to read from Application Properties file
- By default springboot reads configuratoin from src/main/resources/application.properties
- You can define ANY custom properties in this file
- Your spring boot app can access properties using @Value
1
2
coach.name=Mickey Mouse
team.name=The Mouse Club
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// inject the values
@Value("${coach.name}")
private String coachName;
@Value("${team.name}")
private String teamName;
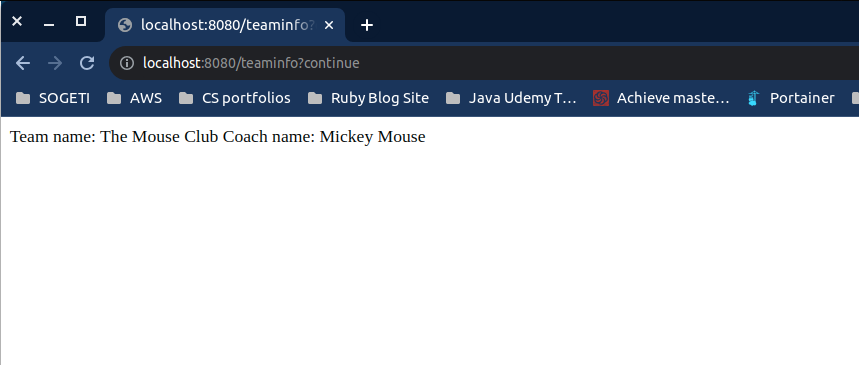
// /teaminfo displays the values we injected from the .properties file
@GetMapping("/teaminfo")
public String teamInfo(){
return "Team name: %s Coach name: %s".formatted(teamName, coachName);
}
Common Springboot application properties
Grouped into the following categories
| Categories |
|---|
| Core |
| Web |
| Security |
| Data |
| Actuator |
| Integration |
| DevTools |
| Testing |
1
server.port=8080
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.