Section 13. (Nested Classes and types) Udemy - Java Programming Masterclass
Git
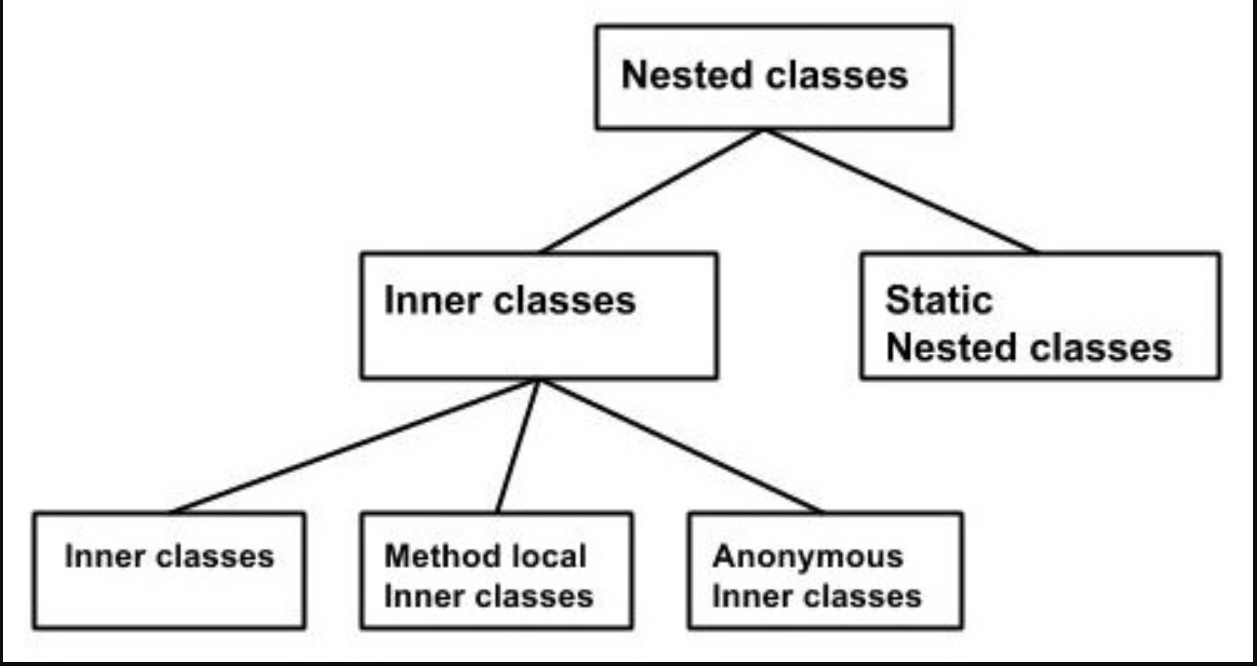
Nested Classes
When to use nested classes
- when your classes are tightly coupled, meaning their functionality is interwoven
4 types of Nested classes
- Static Nested class
- Instance or inner class
- local class
- anonymous class
JDK versions
- Before JDK16, only static nested classses were allowed to have static methods
- As of JDK16, all four types of nested classes can have static members of any type, including static methods
Static nested class
- a class enclosed in another class, declared as static
- access to the static nested class requires the outer class name as part of the qualifying name
- This class has the advantage of being able to access private attributes on the outer class.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
class A {
private String name;
public A(String name){
this.name = name
}
// static class
static class B{
public void test(A a){
System.out.println(a.name); // we can access the private field "name" because we are in a static nested class
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
class Main{
public static void main(String... args){
A.B b = new A.B();
b.test(new A("Tresten"));
}
}
Inner classes
- non-static classes, declared on an enclosing class, at the member level
an inner class has access to instance members, including private members, of the enclosing class
- to create an instance of an inner class, you must first have an instance of the Enclosing Class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class A{
public class B{
public void printSecret(){
System.out.println("I am a secret, shhh..");
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class Main{
public static void main(String... args){
A a1 = new A();
A.B b1 = a1.new B();
b1.printSecret();
// or all on line line
new A().new B().printSecret();
}
}
Local Classes
- local classes are inner classes, but declared directly in a code block, usually a method body.
- Because of that, they don’t have access modifers, and are only accessible to that method body while executing
- Like an inner class they have access to all fields and methods on the enclosing class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
// outer class
public class A {
private String aName;
public A(String aName) {
this.aName = aName;
}
public void printMessage(){
// local class
class compliment{
private String comp;
public compliment(String comp){
this.comp = comp;
}
public String getComp() {
return comp;
}
}
System.out.println(aName + ", you look " + new compliment("GREAT").getComp());
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class Main{
public static void main(String... args){
A a1 = new A("Tresten");
a1.printMessage(); // output: Tresten you look GREAT
}
}
- As of JDK 16, you can also create a local record, interface and enum type in your method block
- These are all implicityly static types, and therefore arent’ inner classes, or types, but static nested types
Anonymous Class
- a local class that doesn’t have a name
- all of the other nested classes before have been created with a class declaration
- Anonymous classes are created without a class declaration
- Anonymous classes are used a lot less, since the introduction of lambda expressions in jdk 8
- There are a couple of ways to use anonymous classes, I will show two ways below
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class Main{
public static void main(String... args){
var comp = new Comparator<Mammal>(){
@Override
public int compare(Mammal o1, Mammal o2) {
return o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());
}
};
}
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.