AWS cloud practicioner
Link to certification!!!!
AWS Notes
Cheat Sheet resources
Service level agreement
- service level agreements are used for describing what you get for aws in resources and what aws promoises in return whether it be a certain number for HA, DR or fault tolerance
AWS resources
- AWS Labs
- Get hands on learning with aws resources for free
- aws labs
AWS Well-Architected Framework
- Security
- Reliability
- Performance Effeciency
- Cost optimization
- Operational excellence
AWS Account ID
- every aws account has a unique Account ID
- composed of 12 digits
- used when
- logging in with a non-root user account
- support cases
- it is generally good practice to keep the account id secret because could be used for malicious actions
Amazon Resource Names (ARN)
- uniquely identify aws resources. ARN’s are required to specify a resource unambiguously across all of AWS
- can contain a wildcard asterick, typically usefull for policies to specify a group of things
- arn:aws:iam::123456789012:user/Development/product_1234/*
- ARN’s have the followinng variations
- arn:partition:service:region:account-id:resource-id
- arn:partition:service:region:account-id:resource-type/resource-id
- arn:partition:service:region:account-id:resource-type:resource-id
- Partition
- aws - aws regions
- aws-cn - china regions
- aws-us-gov - AWS govcloud regions
- Service
- ec2
- s3
- Regions
- us-east-1
- us-central-1
- Resource ID
- Could be a number, name or path
- user/Bob
- instance/i-1232751232382
Examples
- S3 bucket arn
- arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket
- doesn’t contain region, account-id because s3 buckets are in every region and account id because it is the current user
- arn:aws:s3:::my-bucket
- Load balancer
- arn:aws:elasticloadbalancing:us-east-2:123456789101112:loadbalancer/app/my-web-server/1231828182323
IAM Instance Profile
- An AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) instance profile is a secure way to grant AWS services or applications running on Amazon EC2 instances temporary credentials that allow them to access other AWS resources. It’s essentially a container for an IAM role that you can associate with an EC2 instance during launch. This role specifies what permissions and access policies are granted to the EC2 instance or the applications running on it.
AWS Policies
- policies are used to define permissions and access control for various aws resources.
- these policies can be fine-grained or umbrella multiple resources
- policies in AWS are written in JSON format
There are several types of policies used in AWS
- IAM (Identity and access management)
- These policies are used to control access to AWS resources for individual users, groups, or roles. IAM policies define the permissions that are granted or denied for specific actions on specific resources. They are attached to IAM entities, such as users, groups, or roles.
- Resource-based policies
- These policies are associated directly with AWS resources such as S3 buckets, Lambda functions, and SQS queues. They define permissions for other AWS identities to access the resources. For example, you can use a resource-based policy on an S3 bucket to allow a specific IAM user from another AWS account to access the contents of the bucket.
- SCP (Service Control Policies)
- SCPs are used within AWS Organizations to manage permissions across multiple AWS accounts in an organization. SCPs define the maximum permissions that can be applied to an account or organization unit (OU) within the organization.
- Assume Role Policies
- When using IAM roles to grant temporary permissions to an entity (such as an AWS service or a federated user), an assume role policy is attached to the role. It specifies which principal (AWS service or federated user) is allowed to assume the role and under what conditions.
- IAM (Identity and access management)
AWS Global Infrastructure
globally distributed hardware and datacenters that are physically networked together to act as one large resource for the end user customer
Global Infrastructure is comprised of (These numbers are constantly changing)https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/
- 25 Launched regions
- 81 Availability zones
- 108 Direct Connection Locations
- 275+ Points of Precense
- 11 Local zones
- 17 Wavelength zones
AWS Regions
- AWS has the concept of a Region, which is a physical location around the world where we cluster data centers. We call each group of logical data centers an Availability Zone. Each AWS Region consists of a minimum of three, isolated, and physically separate AZs within a geographic area. Unlike other cloud providers, who often define a region as a single data center, the multiple AZ design of every AWS Region offers advantages for customers. Each AZ has independent power, cooling, and physical security and is connected via redundant, ultra-low-latency networks. AWS customers focused on high availability can design their applications to run in multiple AZs to achieve even greater fault-tolerance. AWS infrastructure Regions meet the highest levels of security, compliance, and data protection.
AWS Availability Zones
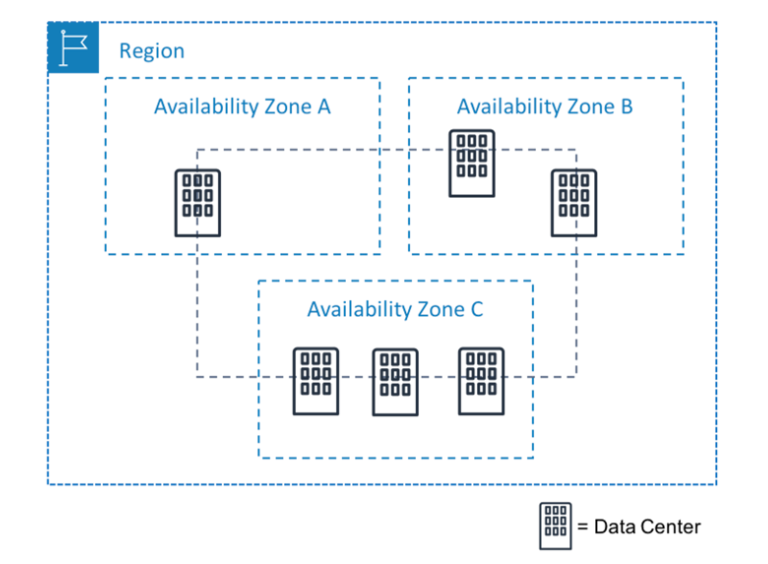
- An Availability Zone (AZ) is one or more discrete data centers with redundant power, networking, and connectivity in an AWS Region. AZs give customers the ability to operate production applications and databases that are more highly available, fault tolerant, and scalable than would be possible from a single data center. All AZs in an AWS Region are interconnected with high-bandwidth, low-latency networking, over fully redundant, dedicated metro fiber providing high-throughput, low-latency networking between AZs. All traffic between AZs is encrypted. The network performance is sufficient to accomplish synchronous replication between AZs. AZs make partitioning applications for high availability easy. If an application is partitioned across AZs, companies are better isolated and protected from issues such as power outages, lightning strikes, tornadoes, earthquakes, and more. AZs are physically separated by a meaningful distance, many kilometers, from any other AZ, although all are within 100 km (60 miles) of each other.
GovCloud (US)
- FedRAMP
- Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program
- US government that provides a standardized approach to security assessment, authorization, and continus monitoring for cloud products and services.
- What is GovCloud?
- A cloud service provider (CSP) generally will offer an isolated region to run FedRAMP workloads
- AWS GovCloud Regions
- Allows customers to host sensitive Controlled unclassified informtation and other types of regulated workloads
- Govcloud regions are only operated by employees who are u.s citizens and on u.s soil
- They are only accessible to U.S entities and root account holder who pass a screening process Customers can architect secure cloud solutions that comply with:
- FedRAMP high baseline
- DOJ’s Criminal Justice information Systems (CJIS) Security Policy
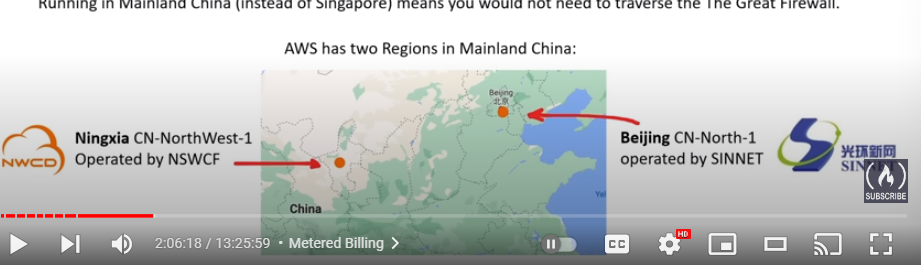
AWS China
- aws cloud offerings for mainland china
- china is completely isolate intentionally from AWS Global to meet regulator compliance for mainland china
- amazonaws.cn
- Not all services are available in china (ex. Route 5)
- Running in mainland china (instead of singapore) means you would not need to traverse the Great Firewall
- There are 2 regions
- Ningxia
- CN-Northwest-1
- Operated by NSWCF
- Beijing
- CN-North-1
- Operated by NSWCF
- Ningxia
Sustainablilty
- Amazon co-founded the Climate Pledge to achieve Net-Zero Carbon Emissions by 2040 across all amazon businesses
- https://sustainability.aboutamazon.com/products-services/the-cloud?energyType=true
- Renewable Energe
- working towards having their AWS Global infrastructure powered by 100% renewable energy by 2025
- Cloud Efficiency
- aws infrastructure is 3.6 times more energy efficient than the median of U.S. enterprise data centers surveyed
- Water Stewardship
- technology to cool the datacenters use of recycled water for cooling purposes
AWS Ground Station

fully managed service that lets you control satellite communications, process data, and scale your operations without having to worry about building or managing your own ground station infrastructure
- used for
- Weather forecasting
- surface imaging
- communications, video broadcasts
- to use ground station:
- schedule a contact (select satellite, start and end time, and the ground location)
- use ec2 instances that will uplink and downlink data during the contact or receive downlinked data in the aws s3 bucket
AWS Outposts
fully managed service that offers the same AWS infrastructure, aws service, api’s, and tools to virtually any datacenter, co-location space, or non-premises facility for a truly consistent hybrid experience
AWS Outposts is a rack of servers running AWS infrastructure on your phyiscal location
comes with the rack server and server
AWS Outposts comes in 3 form factors
- 42U
- 1U
- 2U
Cloud Architecture Teminologies
- Solutions Architect
- tech role that architects a solution using multiple systems via researching, documentation, experimentation
- Cloud Architect
- focused solely on the cloud solutuion
- Availability
- your ability to ensure a service remains available (High Availability HA)
- Scalablility
- your ability to grow rapidly or unimpeded
- Elasticity
- Your ability to shrink and grow to meet the demand
- Fault tolerance
- your ability to prevent a failure
- Disaster recovery
- your ability to recover from a failure (Highly Durable DR)
- Business factors you should always keep in mind
- Security - How secure is this solution?
- Cost - How much is this going to cost
High Availability
your ability for your service to remain available by ensuring there is no single point of failure and/or ensure level of performance
Run your workload across multilple Availability zones ensures if 1 or 2 AZ’s become unavailable your service/applications remains available
Elastic Load Balancer
- A load balancer allows you to evenly distribute traffic to multiple servers in one or more datacenters. If a datacernter or server becomes unavailable, the load balancer will route the traffic to the other working datacenter and servers
High Scalability
your ability to increase your capacity based on the increasing/decreasing demand in traffic, memory and computing power
2 types of scaling
- Vertical Scaling
- Upgrade to a bigger server, ex. better cpu, more ram
- Horizontal Scaling
- Adding more servers of the same size, compute devices to distribute the load to
- Typically preferred because helps with HA
- Vertical Scaling
High Elasticity
your ability to automatically increase/decrease your capacity based on the current demand of traffic, memory and computing power
- Horizontal scaling
- Scaling out
- add more servers of the same size
- Scaling in
- removing underutilized server of the same size
- Scaling out
Typically done with Horizontal scaling because vertical scaling is generally hard for traditional architecture so you’ll usually only see horizontal scaling described with elasticity
- Auto Scaling Groups (ASG)

- an AWS feature that will automatically add or remove servers based on scaling rules you define based on metrics
Fault Tolerance
ability for your service to ensure there is no single point of failture. Preventing the chance of failure
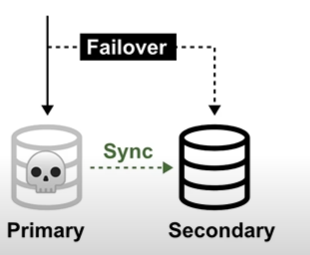
Fail-overs is when you have a plan to shift traffic to a redundant system in case the primary system fails
- a common example is having a copy (secondary) of your database where all ongoing changes are synced. The secondary system is not in-use until a fail over occurs and it becomes the primary database
High Durablility (DR)
ability to recover from a disaster and prevent the loss of data. Solutions that recover from a disaster is known as Disaster Recovery (DR)
- Common questions
- Do we have a backup?
- How fast can you recover with the backup
- Does you backup still work?
- How do you ensure current live data is not corrupt
- Cloud Endure Disaster Recovery
Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
A business continuity plan is a document that outlines how a business will continue operating during an unplanned disruption in services
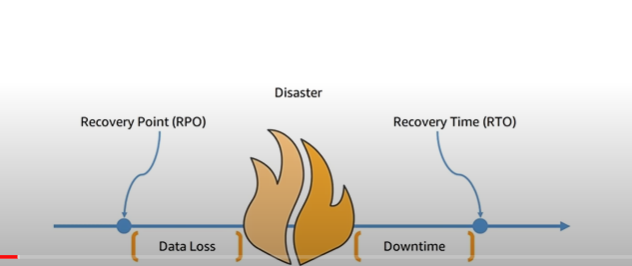
- a BCP will define the Recovery point (RPO) and Recovery time(RTO)
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
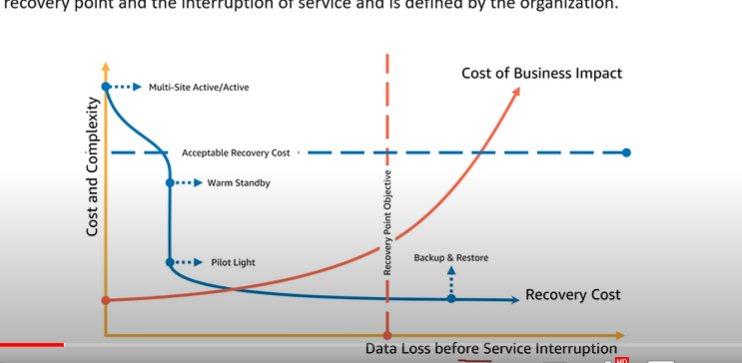
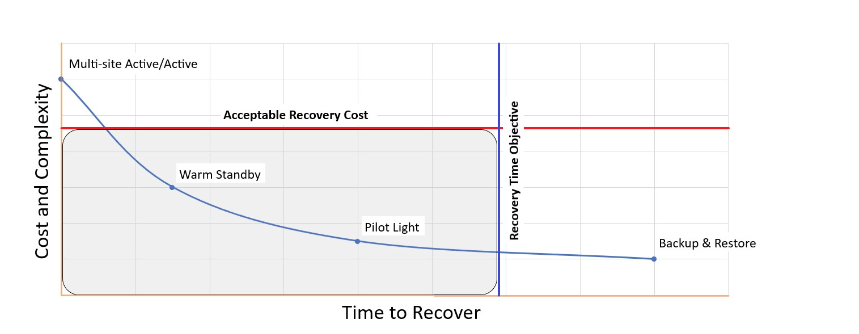
Disaster Recovery Options
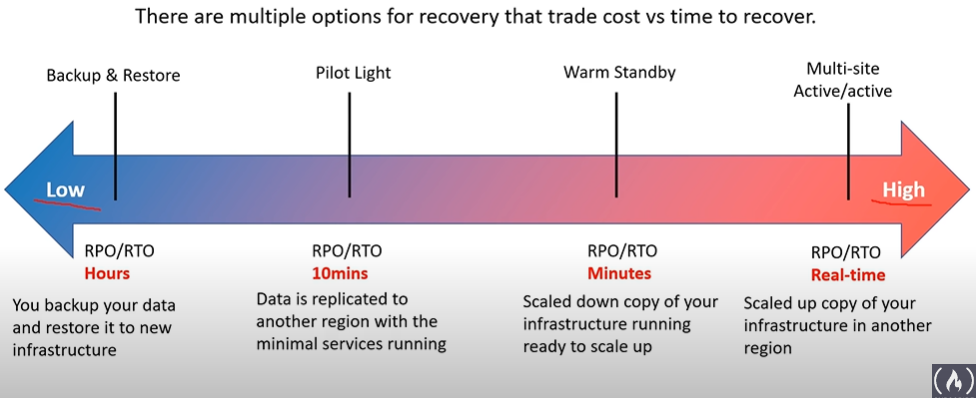
- backing up you data and restoring it new infrastructure is a lot less work and cost effective as opposed as always having a scalled up copy of your infrastructure in another aws regions if the other was to go down
Powershell cloudshell
- by default the cloudshell uses linux terminal
How to use powershell in the cloudshell
pwsh- switch to the powershell shell
Install-Module -Name AWS.Tools.Installer -Force- install the powershell aws installer
Install-AWSToolsModule AWS.Tools.Lambda- install any of the aws modules you would like, in this case it would be installing the lambda module commands
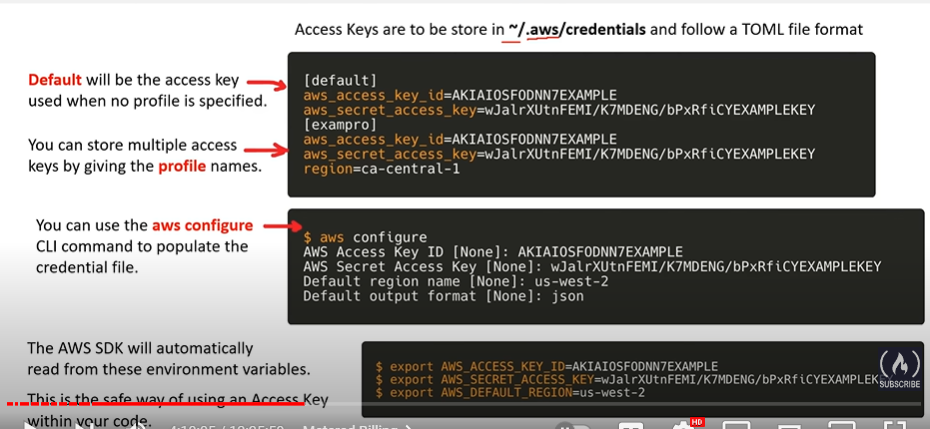
Configuring AWS Cli
- first make sure the aws cli is installed on your system
- go to iam the user you would like to use for the cli
- click on
Create access keyin the iam menu aws configure- paste in the user id and the secret key from the step above
- you can edit and add additional profiles in ~/.aws/credentials
Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Aws has two offerings
- AWS CloudFormation (CFN)
- What you see is what you get
- More verbose, but zero chance of mis-configuration
- Json, YAML, XML
- AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK)
- You say what you want, and the rest is filled in implicit
- less verbose, you could end up with misconfiguration
- Does more than Declarative
- Python, ruby, php, javascript, etc…
- AWS CloudFormation (CFN)
AWS CloudFormation
- Allows you to write Iac in either a Json or Yaml file
- easier for devops engineers who do not have a background in web programming languages
- is simple but can lead to large files or is limited in some regard to creating dynamic or repeatable infrastructure compared to CDK
AWS Toolkit for VSCode
plugin to create, debug, deploy aws resources
what you get
- aws explorer
- explore a wide range of aws resources to your linked aws account
- aws cdk explorer
- allows you to expore your stacks defined by your cdk
- aws elastic container service
- provides intellisense for ecs task-definitions files
- Serverless applications
- create, debug, deploy serverless applications via SAM and CFN
- aws explorer
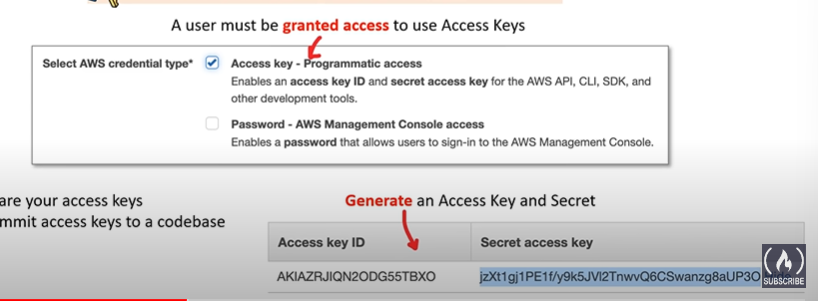
Access Keys
- Key and secret required to have programmatic access to AWS resources. Like when interacting with the aws api outside of the aws management console.
commonly referred to as AWS Credentials
- Things to know about access keys
- Do Not share your access keys
- Do Not commit access keys to a codebase like git
- you can have 2 active access keys
- you can deacticate access keys
- access keys have whatever access a user has to a aws resource
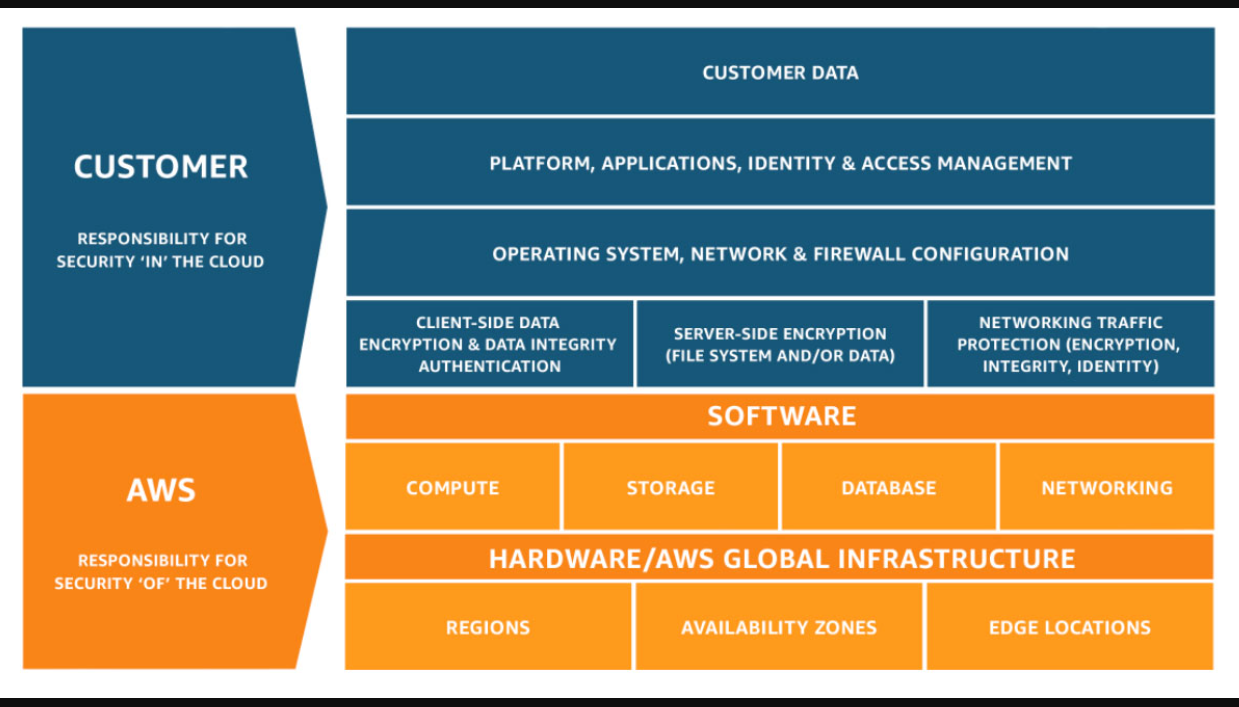
Shared Responsiblity Model
Cloud security framework that defines the security obligations of the customer versa the cloud service provider (CSP)
each CSP has their own variant of the Shared responsiblity model by they are all generally the same
- In / Of
- Customers are responsible for the data in the cloud
- AWS is responsible of the resources/hardware of the cloud
EC2
- Highyly configurable virtual machine commonly referred to as instance
- Allows you to attach multiple virtual hard-drives for storage Elastic Block Store (EBS)
- Allows you to pick an AMI (Amazon machine image)
- pre-defined configuration for a vm
- 4 ways to connect
- EC2 instance connect
- session manager
- ssh client
- ec2 serial console
- considered the backbone of aws because a majority of aws services are using ec2 under the hood like S3, RDS, DynamoDB, Lambdas
Pricing
- Different types of pricing
- On-demand
- low cost and flexible
- per hour or the second
- short-term, spikey, unpredictable workloads
- cannot be interrupted
- least commitment
- Spot
- up to 90% off
- request spare computing capacity
- flexible start and end times
- can handle interruptions (server starting and stopping randomly) biggest saving
- Reserved
- up to 75% off
- steady state or predictable usage
- commit to ec2 over a 1 or 3 year term
- can resell unused reserved instances
- best long term
- Dedicated
- dedicated server
- can be on-demand or reserved or spot
- most expensive
- On-demand
- Another way to save but can be used for more than just ec2 is AWS Savings Plan
EC2 Instance Families
- General Purpose
- A1, T2, T3, T3A, T4G, M4, M5, M5a, M5n, M6zn, M6g, M6i, Mac
- use cases - web servers, code repo’s
- Compute Optimized
- C5, C4, Cba, C5n, C6g, C6gn
- use cases - high performance processor, scientific modeling, dedicated gaming servers
- Memory Optimizied
- R4, R5, R5a, R5b, R5n, X1, X1e, High Memory, z1d
- use cases - in-memory caches, in memory databases, real time big data analytics
- Accelerated Optimized
- P2, P3, P4, G3, G4ad, G4dn, F1, Inf1, VT1
- Hardware accelerators, co-processors
- use cases - machine learning, computational finance, speech recognization
- Storage Optimized
- I3, I3en, D2, D3, D3en, H1
- use cases - high sequential read / write access to very large data sets on local storage
EC2 Instance Types
- nano, micro, small, medium, large, xlarge, 2xlarge, 3xlarge, 4xlarge, 8xlarge
- instance size generally double in prices and key attributes
- they generally double in price as you go up
AWS Container services
- Elastic Container Service (ECS)
- container orchestration service
- Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
- repository for container images
- ECS Fargate
- serverless orchestration container services
- Elastic Kubernetes Services (EKS)
- fully managed kubernetes service
High performance computing (HPC)
- Nitro System is a combination of dedicated hardware and lightweight hypervisor enabling faster innovation and enhanced security. All new EC2 instances types use the Nitro System. They are made up by the
- Nitro cards - specialized cards for VPC, EBS and instance storage
- Nitro security chips - integrated motherboart. protects hardware resources
- Nitro hypervisor - lightweight hypervisor memory and cpu allocation Bare-metal like performance
- Bare metal instance
- you can launch ec2 instance that have no hypervisor so you can run workloads directly on the hardware for maximum performance and control. The M5 and R5 ec2 instances run are bare metal.
- What is High Performance Computing (HPC)
- a cluster of hundreds of thousands of servers with fast connections between each of them with the purpose of boosting computing capacity.
- AWS Parallel Cluster
- an AWS-suported open source cluster management tool that makes it easy for you to deploy and manage HPC clusters on AWS
- Tool is used in python
Edge Computing
- What is edge computing
- When you push your computing workloads outside of your networks to run close to the destination location.
- ex. Pushing computing to run on phones, IoT Devices, or external servers not within your cloud network
- When you push your computing workloads outside of your networks to run close to the destination location.
- What is hybrid computing
- when you’re able to run workloads on both your on-premise datacenter and AWS Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- AWS Outposts
- physical rack of server that you can put in your datacenter. Allows you to use aws api and services such as ec2 right in your datacenter
- AWS Wavelength
- allows you to build and launch your applications in a telecom datacenter. By doing this your applications will have ultra-low latency since they will be pushed over a 5G network and be closest as possible to the end user
- VMWare Cloud on AWS
- allows you to manage on-premise vm’s using VMWare as EC2 instances
- The datacenter must be using VMWare for Virtualization
- AWS Local Zones
- edge datacenters located outside of an AWS region
- used so you can use AWS closer to end destination
Cost management
- Cost Management
- How do we save money?
- Capacity Management
- How do we meet the demand of traffic and usages though adding or upgrading servers?
- EC2 Spot Instances, Reserved Instanced and Savings Plan
- Ways to save on computing, by paying up in full or partially, by commiting to yearly contracts or by being flexible about availability and interruption to computing service
- AWS Batch
- plans, schedules and executes your batch computing workloads across the full range of AWS compute services, can utilize spot instance to save money
- AWS Compute Optimizer
- suggests how to reduce costs and improve performance by using machine learning to analyze your previous usage history
- EC2 Autoscaling Groups (ASGs)
- Automatically adds or removes ec2 instances to meet the current demand of traffic, will save you money and meet capacity, since you only run the amount of servers you need
- Elastic Load Balancer (ELB)
- Distributes traffic to multiple instances, can re-route traffic from unhealthy instances to healthy ones. Can route traffic to ec2 instances running in different AZ
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk (EB)
- for easiyly deploying web-applications without having developers having to worry about setting up underlying aws resources. Simliar to Heroku
Types of Storage Services
- Elastic Block Store (EBS) - BLOCK

- Block data is split evenly into split blocks directly accessed by the OS
- supports only a single write volume
- When you need a virtual hard drive attached to a single ec2 instance
- FC (Fibre Channel) and iSCSI are two different storage protocols used in computer networks to connect and access block storage devices.
- AWS Elastic File Storage (EFS) - FILE
- AWS Simple Storage Service (S3) - OBJECT

- supports multiple reads/writes (no locks)
- no file limit or storage limit (scales up)
- you can only have 100 buckets
- Buckets hold objects and may also have folders which in turn hold objects
- S3 is a universal namespace so bucket names must be unique (think like having a domain name)
- Https/API’s
- You can hold objects from 0 bytes to 5 terabytes in size
- Supports server side encryption SSE (encryption done by s3)
- only one server side encryption option per object
- S3 Storage Classes
- AWS Storage Gateway
- hybrid cloud storage service that extends yoiur on-premise storage to cloud
- File Gateway
- extends your local storage to s3
- Volume Gateway
- caches your local drives to s3 to have continious backup of local files in the cloud
- Tape Gateway
- stores files onto virtual tapes for backing up your files on very cost effective long term storage
- AWS Backup
- a fully managed backup service that makes it easy to centralize and automate the backup of data across multiple aws services like ec2, rds, dynamodb, efs. You create the backup plan.
- AWS FSx
- Windows/Linux file server allows you to mount Fsx to your server
AWS Snow Family
- storage and compute devices used to physically move data in or out of the cloud when moving data over the internate or private connection it is too slow, difficult or costly.
- used for migrating large amounts of data to the cloud
- Data is devlivered to s3

Data Warehouses
- A relational datastore for analytic workloads, which is generally column-oriented data-store
- Companies will have terabytes and millinos of rows of data and they will need a fast way to be able to produce analytics reports
- Data warehouses generally perform aggregation or a grouping of data to find a total or average
- optimized around columns
DynamoDB
- a serverless nosql key/value and document database
- designed to scale billions of records with guaranteed consisten data return in at least a second.
- you don’t have to worry about managing shards
- AWS’s flagship database service, whenever you think of databases on aws you should first think of DynamoDb
DocumentDB
- NoSQL document database that is MongoDB compatible
- when you want to use MongoDB
Amazon Keyspaces
- fully managed Apache Cassandra database
- NoSql key/value database
Relational Database Service (RDS)
- relational db service
- supports multiple sql engines
- most common type of database
- MySQL, MariaDB, Postgres, Oracle, Microsoft sql server, Aurora
Aurora
- Relational db
- fully managed db of either mysql (5x faster) and postgres (3x faster)
Aurora Serverless
- serverless on-demand version of aurora
- you get the benefits of aurora but can trade off to have cold starts or you don’t have lots of traffic demand
RDS on VMWare
- allows you to deploy rds supported engines to an on-premise data-center
Redshift
- petabyte-size data-warehouse
- hot online analytical processing (OLAP)
Elasticache
- managed db in-memory and caching open source database redis or memcached
- when you want to improve the performance of applications by adding a caching layer in front of web-server or database
Neptune
- Managed graph database
- when you want to understand connections between data ex. (social media, mapping fraud rings, maps)
AWS Timestreams
- fully managed time series database
- think of devices that send lots of data that are time sensitive such as iot devices
- when you need to measure how things change over time
Amazon Quantum Ledger Database
- fully managed **ledger database that provides transparent, immutable and crytographically variable transaction logs.
Database Migration Service (DMS)
- a db migration service that allows you to migrate from
- on-prem to aws
- sql to no-sql
Cloud-Native Networking services
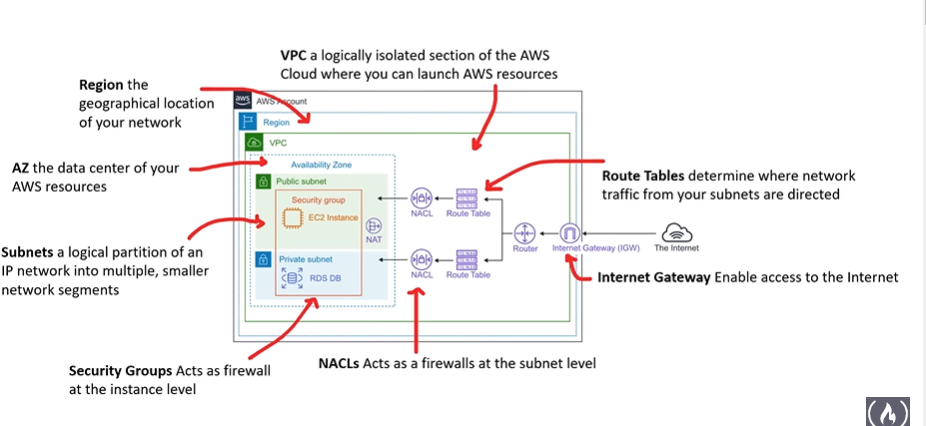
Most aws resources require that you deploy them in a VPC (virtual private cloud)
In order for you or an application to access your application on your vpc you must have an Internet Gateway
Route Tables determine where network traffic from your subnets are directed
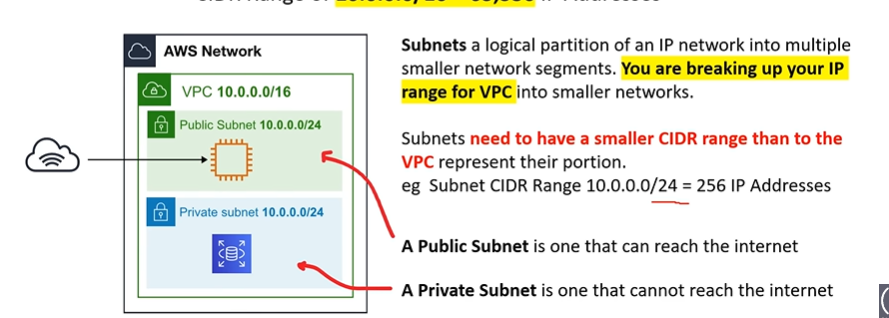
Subnets - a logical partition of an ip network into multiple, smaller network segments
- NACL’s (Network access control list) acts as firewalls at the subnet level
- A network access control list (ACL) allows or denies specific inbound or outbound traffic at the subnet level
- There is no additional charge for using network ACLs.
- Security Groups - act as a firewall at the instance level
Network Access Control List (NACL)
A network access control list (ACL) allows or denies specific inbound or outbound traffic at the subnet level
There is no additional charge for using network ACLs.
- By default denies all inbound traffic and allows all outbound traffic
- this is used so that the security groups can allow specific traffic like ssh or https
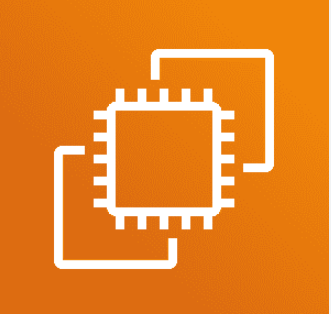
- The following diagram shows a VPC with two subnets. Each subnet has a network ACL. When traffic enters the VPC (for example, from a peered VPC, VPN connection, or the internet), the router sends the traffic to its destination. Network ACL A determines which traffic destined for subnet 1 is allowed to enter subnet 1, and which traffic destined for a location outside subnet 1 is allowed to leave subnet 1. Similarly, network ACL B determines which traffic is allowed to enter and leave subnet 2.
- Your VPC automatically comes with a modifiable default network ACL. By default, it allows all inbound and outbound IPv4 traffic and, if applicable, IPv6 traffic.
Internet Gateway
An internet gateway is a horizontally scaled, redundant, and highly available VPC component that allows communication between your VPC and the internet
An internet gateway enables resources in your public subnets (such as EC2 instances) to connect to the internet if the resource has a public IPv4 address or an IPv6 address. Similarly, resources on the internet can initiate a connection to resources in your subnet using the public IPv4 address or IPv6 address. For example, an internet gateway enables you to connect to an EC2 instance in AWS using your local computer.
An internet gateway provides a target in your VPC route tables for internet-routable traffic
Route Tables
- A route table contains a set of rules, called routes, that determine where network traffic from your subnet or gateway is directed.
AWS Security Groups
Feature for ec2 instances
Acts as a firewall at the instance level
Implicitly denies all traffic
You create only ALLOW rules
A security group controls the traffic that is allowed to reach and leave the resources that it is associated with. For example, after you associate a security group with an EC2 instance, it controls the inbound and outbound traffic for the instance. You can associate a security group only with resources in the VPC for which it is created.
AWS DirectConnect
AWS PrivateLinks
VPC interface endpoints
keeps traffic within the AWS Network and not travers the internet to keep traffic secure
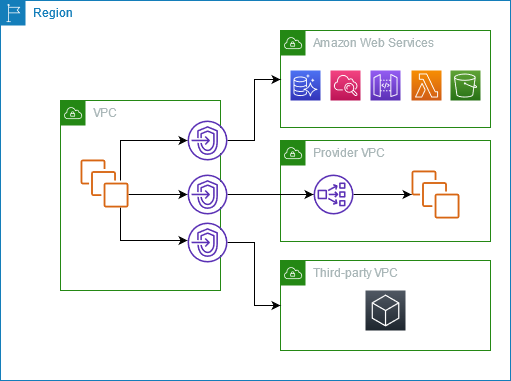
privately connect your VPC to services as if they were in your VPC. You do not need to use an internet gateway, NAT device, public IP address, AWS Direct Connect connection, or AWS Site-to-Site VPN connection to allow communication with the service from your private subnets. Therefore, you control the specific API endpoints, sites, and services that are reachable from your VPC.
- In the following diagram, the VPC on the left has several EC2 instances in a private subnet and three interface VPC endpoints. The top-most VPC endpoint connects to an AWS service. The middle VPC endpoint connects to a service hosted by another AWS account (a VPC endpoint service). The bottom VPC endpoint connects to an AWS Marketplace partner service.
Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
Logically isoated sections of the aws network where you launch your aws resources
you choose a range of ips using CIDR Range
- public subnet is one that can reach the internet
- private subnet is one that cannot reach the internet
Elastic IP address
- Used in EC2
- Allows you to assign a static ip address to an ec2 instance that will stay the same after restarts and shutdowns
- this is important because by default ec2 instances get a dynamic ip address that is subject to change
AMI (Amazon Machine image)
- ec2 feature
- contains all necessary info needed to launch an ec2 instance
- it is a block level disk image of the os drive
Launch template
- ec2 feature
- a cookie cutter that you use to launch new instances with an auto-scaling group
- cool because you have can have versioning of a single launch tempalte
Auto scaling groups
- ec2 feature
- An Auto Scaling group is a collection of Amazon EC2 instances that are treated as a logical unit. You configure settings for a group and its instances as well as define the group’s minimum, maximum, and desired capacity. Setting different minimum and maximum capacity values forms the bounds of the group, which allows the group to scale as the load on your application spikes higher or lower, based on demand. To scale the Auto Scaling group, you can either make manual adjustments to the desired capacity or let Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling automatically add and remove capacity to meet changes in demand.
Elastic Load balancer
- distributes traffic between different instances based on demand and resources and health
- requrie a target group that allows you to define where you traffic gets distributed upon when the load balancer is in progress
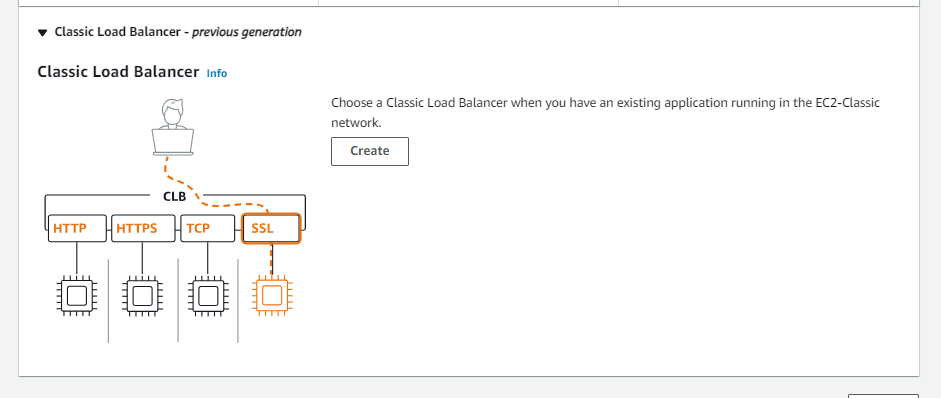
Target Groups
- ELB feature
- A target group is required when creating ELB’s
- this is because the elb has to know where it has to distribute the traffic upon and how
- There are 4 target types
- Instances
- Ip addresses
- Lambda function
- Application load balancer
AWS Free tier
- includes offers that expire 12 months after sign-up or some that never expire
#### 12 months after sign up include - ec2 750 hours - linux t2 micro
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- s3 5Gb
- rds
- 750 hours
- 20gb db storage
- 20gb backup storage
- cloudfront
- 50gb data transfer out
#### Always available free tier - DynamoDb - 200 million requests per month - 25gb indexed data storage - 2.5 million read request
1
2
3
4
5
6
- Glacier
- Retrieve up to l0 gb of you glacier storage per month
- lambda
- 1 million requests per month
- up to 3.2 million seconds of compute time per month
Pricing
- There are three fundamental costs with aws compute, storage, outbound data transfer
- There are no costs for inbound data transfer
- There are also no costs for data transfer between other aws services from within the same region
- Paid by the hour or the second
Price reflected in terms of GB
- Pay as you go (PAYG Model)
- no up-front payment and non long-term commitment
#### Reserved instances (RI) - designed for applications that have steady state, predictable usage or require reserved capacity - 1 or 3 year contracts - they do NOT renew automatically
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
- RI marketplace
- can be sold after they have been active for at least 30 days and once aws has received the upfront payment (if applicable)
- Regional RI vs Zonal RI
- 
- formula
- **Term * Class offering * RI Attriutes * Payment options**
- the longer the term the greater the savings
- Classes
- 
- standard
- up to 75% off
- Convertible
- up to 54% off
- RI Attributes
1. instance types
- ex. t2 micro
2. region
- ex. Us-East-1
3. tenancy
- ex. single-tenant
4. platform
- linux, windows
- payment options
- All upfront
- Partial upfron
- no upfront
- Limits
- Per month
- 20 regional ri per region
- 20 zonal ri per az
Savings Plans
- similiar discounts as reserved instances but simplifies the purchasing process
- 1 or 3 year contracts
all upfront, partial upfront, no upfront
3 types of savings plans
- Compute savings plans
- up to 66%
- EC2 instance savings plans
- up to 72%
- sagemaker savings plans
- up to 64%
- Compute savings plans
Security
#### Zero trust model - “trust no one, veryify everything.” - Network centric (Old-way) - traditional firewalls, vpns since few employees or workstations outside of the office - Identity centric (New-way) - bring your own device - remote workstations much more common
#### Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) - providing a user the least amount of permissions to perform an operation or action - JEA (Just enough access) - JIT (Just in time)
Security Services
- AWS GuardDuty
- Detects suspicious or malicious activity based on cloudtrail and other logs
- Amazon Detective
- Used to analyze, investigate security issues (can ingest from GuardDuty)
IAM Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- How do configure permissions
- Identities
- IAM Users
- IAM Groups
- IAM Roles
Application Integration
app integration is the process of letting two independent apps to communicate and work with each other
workloads encourage systems and services to be loosely coupled
- common design patterns
- queing
- streaming
- pub/sub
- api gateway
- state machine
- event bus
- What is a messaging system?
- asynchronous communication from sender and receiver (producer and consumer)
- what is a Qeueing system?
- messaging system that generally delete messages once they are consumed.
- simple communication. NOT real time
- Have to pull, not reactive
- AWS SQS
- What is Streaming?
- Multiple consumers can react to events (messages)
- Events live in the stream for long periods of time, so complex operations can be applied
- Real time
- AWS Kinesis
- What is pub/sub
- Publish-suscribe pattern
- commonly implemented in messaging systems
- publishers do not send their messages directly to receivers, instead they send it to to a messaging bus
- AWS SNS
- What is a state machine?
- A state machine is an abstract model which decides how one state moves to another based on a series of conditions.
- Like a flow chart
- aws step functions
- coordinate multilple aws serivce into a serverless workflow
- What is an Event bus?
- an event bus receives events from a source and routes events to a target based on rules
- AWS Event Bridge
- serverless event bus service that is used for application integration by streaming real-time data
- previously known as Amazon Cloudwatch
AWS API Gateway

- What is an API gateway
- program that sits between a single entry-point and multiple backends
- allows for throttling, logging, routing logic or formatting of the request and response
- a solution for creating secure apis in your cloud environment at any scale
- What is an API gateway
Simple Notification Service (SNS)
- pub-sub messaging system
- sends notifications in many formats (email, http, sms, etc..)
- push messages which are sent to subscribers
Simple Queue Service (SQS)
- queing messaging service
- sends events to messaging queue
- Other apps pull from the queue for messages
- commonly used for background jobs
Step Functions
- state machine service
EventBridge (Cloudwatch)
- serverless event bus
- makes it easy to connect apps together from your own app
Kinesis
- real-time streaming
- producers send data to the stream, multiple consumers consume within the stream
Amazon MQ
- Managed message broker service
- uses Apache ActiveMQ
Managed Kafka Service (MSK)
- fully managed Apache Kafka service
- platform for building real-time streaming data pipelines
App Sync
- Fully managed GraphQL Service
Kubernetes
- container orchestration system
- pods - a group of one or more containers with shared storage, network resources and other shared settings
- tens to hundreds of services that they need to manage
Podman
- container engine that is OCI compliant
- replacement for docker, because docker introduced the paid model
- daemonless
- allows you to create pods
AWS Config
- Compliance-as-code framework
- allows us to manage change in your aws account
- Per region basis
- Cac (Compliance as code)
AWS Quick Starts
- prebuilt templates to help deploy a wide range of stacks
Tags
- key/value pair assigned to aws resources
Resource Groups
- collection of resources that share one or more tags
Serverless Services
- What is serverless?
- underlying servers, infrastructure and os is taken care of by the CSP.
- Generally Highly available, scalable and cost-efective by default
- pay-for-value
- you don’t pay for idle servers
- scale-to-zero
- resources cost you nothing if not in use
- Dynamodb
- S3
- ECS Fargate
- lambda
- step functions
- auora serverless
- much more…
AWS cloudtrail
- logging by default and will collect logs for the last 90 days
- if you need more than 90 days create a trail
- trails output to s3
- if you need to see a gui output to Amazon Athena
Machine learning and AI services
- AWS Sagemaker
- fully managed build, trail, and deploy ML models at scale
- Amazon CodeGuru
- ML code analysis
- Amazon Lex
- conversation interface service
- Amazon Personalize
- real-time recommendations
- Amazon Polly
- text to speech
- Amazon Rekognition
- image and video recognition service
- Amazokn Transcribe
- speech-to-text service
Amazon Textract - OCR (extract text from scanned documents) service
- Amazon Translate
- Neural ML translation service
- Amazon Comprehend
- Natural language Process (NLP) service
- Amazon Forecast
- time-series forecasting service
- AWS Deep learning AMI’s
- **pre-installed with popular deep learning frameworks
- AWS Deep Learning Containers
- Docker images with pre-installed popular deep learning frameworks and interfaces
- AWS DeepComposer
- ML enabled musical keyboard
- AWS DeepLens
- video camera that uses deep-learning
- AWS DeepRacer
- toy race car
- autonomous driving
- toy race car
- Amazon Elastic inference
- lost cost gpu powered to ec2 instancces to reduce cost of running deep learning by 75%
- Amazon Faud Detector
- fully managed fraud detection a service
- Amazon Kendra
- Enterprise ML search engine service
Aws Cloud Adoption Framework CAF
- whitepaper to help you plan your migration from on-premise to aws
- 6 key areas
- Business perspective
- People perspective
- Governance perspective
- Platform perspective
- Security perspective
- Operations perspective
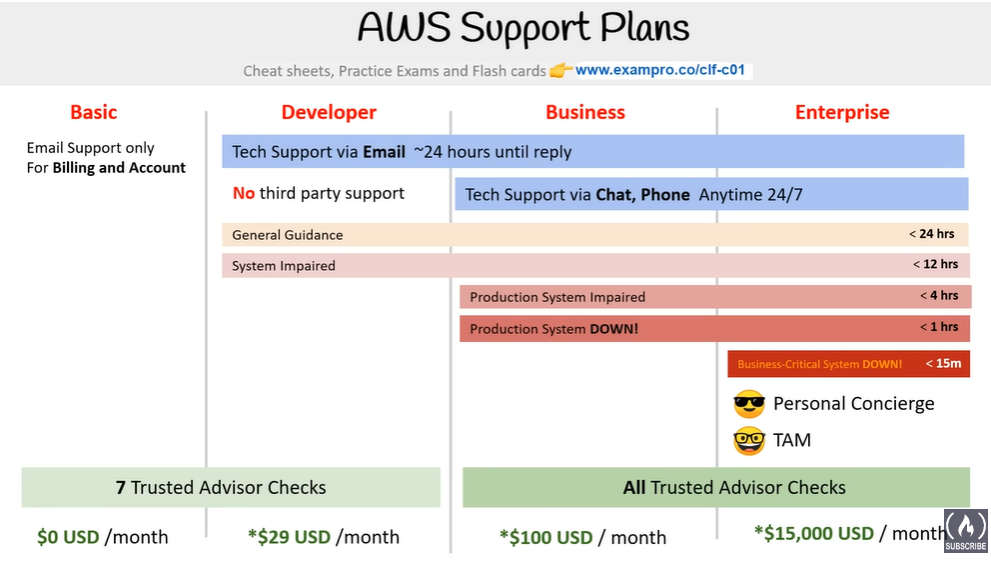
AWS Support plans
AWS Service Health Dashboard
- shows the general status of aws services
AWS Personal Health Dashboard
- provides alerts and guidance
- shows events to help manage active events
AWS Abuse
- AWS Trust & Safety
- team that specifically deals with abuses occuring on the aws platform
- spam, port scanning, ddos